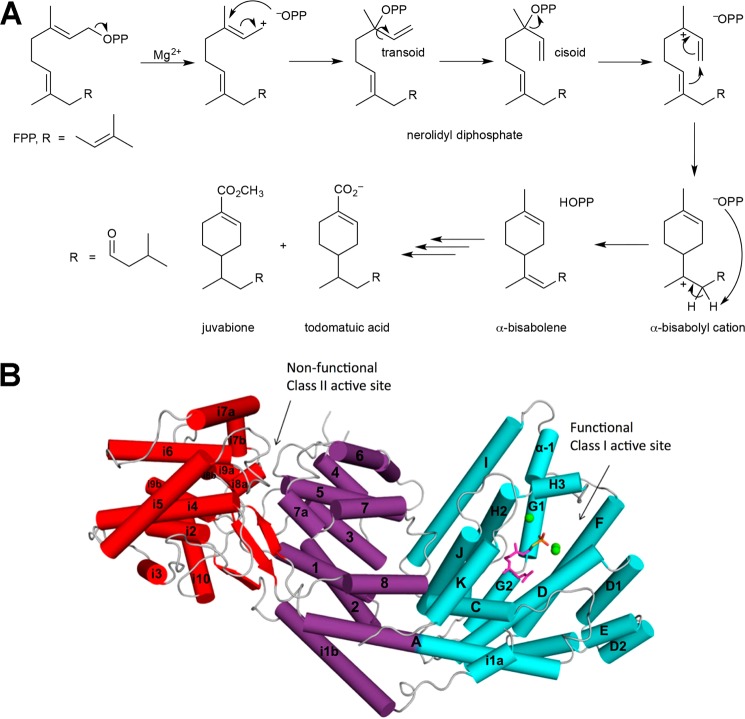
Figure 50.
(A) The catalytic mechanism of α-bisabolene synthase proceeds through a characteristic ionization-recombination-reionization sequence in order to facilitate C1–C6 bond formation. The cyclization product, α-bisabolene, is a biosynthetic precursor of juvabione and todomatuic acid, which mimic insect juvenile hormones. (B) The crystal structure of α-bisabolene synthase reveals αβγ domain architecture. The α domain (cyan) contains the functional class I terpenoid cyclase active site; the βγ domains (purple and red, respectively) are vestigial and have no known catalytic function. Reprinted with permission from ref (46). Copyright 2011 Elsevier.