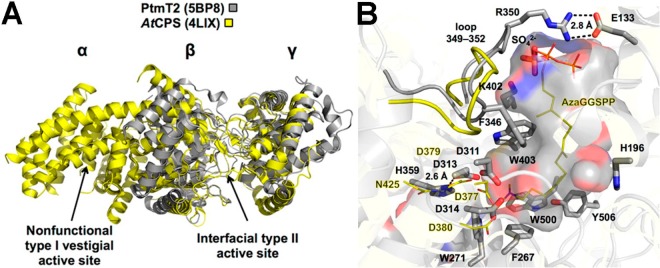
Figure 81.
(A) Superposition of ent-copalyl diphosphate synthase from Arabidopsis thaliana (αβγ domain architecture, yellow) and Streptomyces platensis CB00739 (βγ domain architecture, gray). (B) Superposition of ent-copalyl diphosphate synthase active sites. In the plant enzyme, N425 hydrogen bonds with general acid D379, whereas in the bacterial enzyme H359 hydrogen bonds with general acid D313. Reproduced from ref (435). Copyright 2016 American Chemical Society.