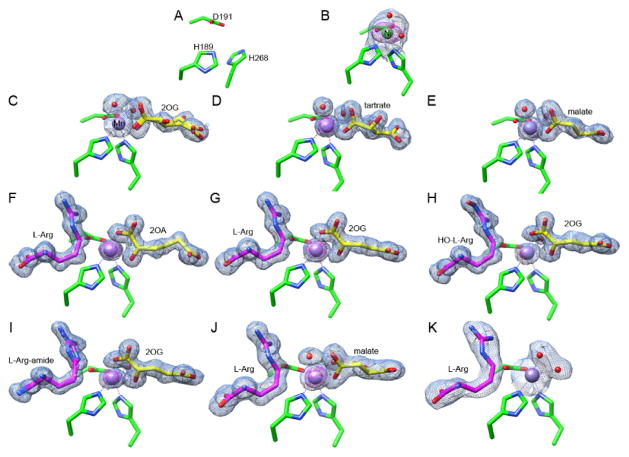
Figure 1.
Active site views of 11 EFE structures. Carbon atoms of the metal-chelating residues (H189, D191 and H268) are shown in green; 2OG, 2OA, malate, or tartrate are depicted in yellow; L-Arg, HO-L-Arg, or L-Arg-amide are illustrated in magenta; Mn and Ni atoms are shown as purple and green spheres. The 2FO - FC maps for metal atoms and ligands are shown as blue meshes at 1 σ. The anomalous maps for metal atoms are shown as magenta meshes at 5 σ. Metal chelation is indicated by dashed lines. Bound water molecules are shown as red spheres. (A) EFE apoprotein. (B) EFE•Ni. (C) EFE•Mn•2OG. (D) EFE•Mn•tartrate. (E) EFE•Mn•malate. (F) EFE•Mn•2OA•L-Arg. (G) EFE•Mn•2OG•L-Arg. (H) EFE•Mn•2OG•HO-L-Arg. (I) EFE•Mn•2OG•L-Arg-amide. (J) EFE•Mn•malate•L-Arg. (K) EFE•Mn•L-Arg.