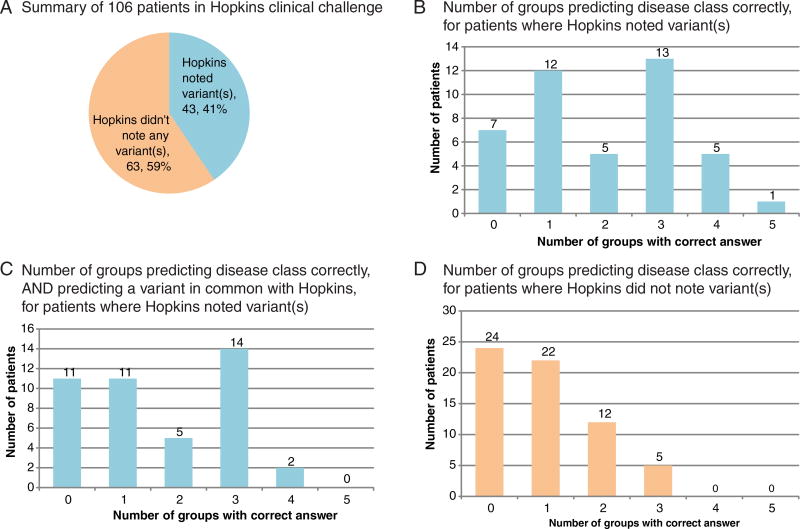
FIGURE 1.
Summary of CAGI-4 Hopkins clinical panel challenge and results. A: One-hundred six patients were included in the study. Hopkins noted at least one variant relevant to the disease class for which the patient was referred in 43 cases, and did not note a variant for the remaining 63 cases. Hopkins noted variants of the following classes: variant of uncertain significance, likely pathogenic, or pathogenic. Clinically, Hopkins would have reported 25/43 as positive and 18/43 as uncertain. B: Among the 43 patients for whom Hopkins had noted a variant, at least one CAGI-4 prediction group predicted the correct disease class in 36 cases, and one patient’s disease class was predicted correctly by all five groups. C: Among the 43 patients for whom Hopkins had noted a variant, at least one CAGI-4 prediction group predicted both the correct disease class and a causal variant noted by Hopkins in 32 cases. D: Sixty-three patients for whom Hopkins did not note a variant were more difficult for CAGI-4 groups to predict: 24were not predicted correctly by any group, and only five patients’ disease class was predicted correctly by three groups (none were predicted correctly by four or more groups)