Figure 3. nucCD24 binds chromatin and its expression enhances growth in vitro and in vivo.
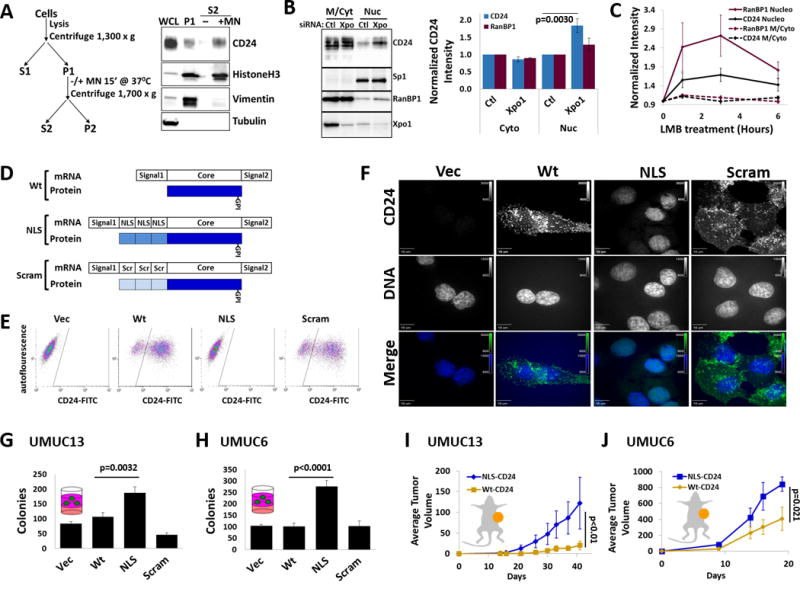
(A) Chromatin isolation strategy and subsequent DNA digestion with micrococcal nuclease (MN). Modified from classic Méndez and Stillman protocol. CD24, HistoneH3 and vimentin were all isolated in the chromatin prep (P1) from UMUC3-Lul2 cells but only CD24 and HistoneH3 are released from the prep (S2) following DNA digestion. (B) Depletion of Xpo1 from UMUC3-Lul2 cells led to an accumulation of CD24 and RanBP1 in the nucleoplasm fraction but no change in Sp1 levels. (C) Inhibition of nuclear export in UMUC3-Lul2 cells by Leptomycin B (LMB) (20nM) also resulted in accumulation of CD24 and RanBP1 in the nucleoplasm fraction. Blot shown in Fig. S4. (D) Schematic of the CD24 cDNA constructs and mature protein products generated in this study to drive CD24 to the nucleus (NLS) or the scrambled (Scram) control. (E) Stable expression of these constructs in MGHU3 cells (which lack endogenous CD24 protein and do not form colonies in soft agar) and subsequent FACS shows that wild-type-CD24 (Wt) and Scram-CD24 (Scram) cells have high CD24 signal on their cell surface while control cells and NLS-CD24 (NLS) cells do not. (F) Immunofluorescence confirms that Wt and Scram-CD24 have identical cellular distribution while NLS-CD24 colocalizes exclusively with DNA (DAPI). Channel intensities are identical across each line for DAPI or CD24 signals. (G) Expression of CD24 constructs in UMUC13 cells, which lack endogenous CD24 protein and which form colonies in soft agar assays, reveals that cells expressing NLS-CD24 form the most colonies. (H) Expression of the CD24 constructs in UMUC6 cells, which express little endogenous CD24 and which form colonies in soft agar assays, reveals that cells expressing NLS-CD24 form the most colonies. (I) UMUC13 cells expressing Wt or NLS-CD24 were injected into the flanks of nude mice and tumor volume analysis revealed that cells expressing NLS-CD24 lead to a tumor growth rate almost 3 times that of cells expressing Wt-CD24. p-value is from two-way RM-ANOVA. (J) UMUC6 cells expressing Wt-CD24 had almost half the tumor growth rate of UMUC6 cells expressing NLS-CD24.
