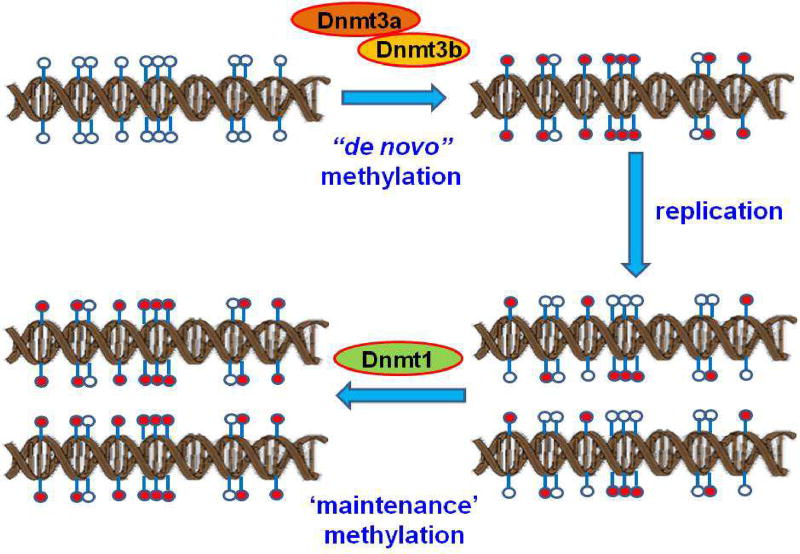
Fig. 3.
Passive DNA demethylation pathway. Passive DNA demethylation is caused by a reduction in activity or absence of Dnmts. Dnmt3a and 3b are responsible for de novo DNA methylation of parent DNA. When methylated DNA is replicated, the daughter strands of DNA are unmethylated. This hemimethylated DNA is recognized by the maintenance DNA methyltransferase1 (Dnmt1) and restores parental DNA methylation patterns through successive rounds of cell division. If Dnmt1 is inhibited or absent when the cell divides, the newly synthesized strand of DNA will not be methylated, and successive rounds of cell division will result in passive demethylation. In this figure, unmethylated CpGs are shown by empty circles, and methylated CpGs are indicated by red circles.