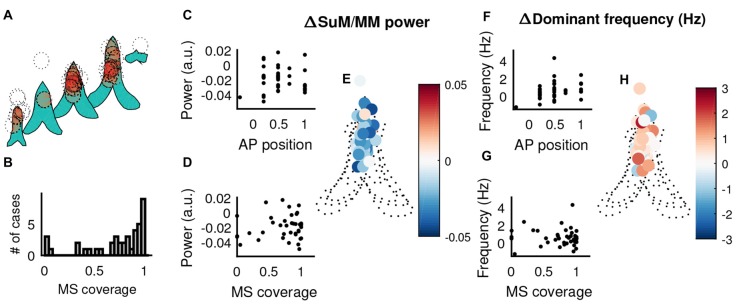
Figure 7.
The influence of MS cannula placement in theta-related changes elicited by MS-inactivation. (A) Liberal estimates of tetracaine spread (1 mm diameter centered on reconstructed cannula tip, dotted circles) and affected areas within the MS (shaded in red) in the coronal plane, across different points on the anterior-posterior axis. (B) Distribution of MS coverage of the 1 mm “circle of influence”. (C) Correlation between the relative change of SuM/MM theta power normalized by HPC theta power change and the recording position in the anterior-posterior axis. (D) Correlation between the relative change of SuM/MM theta power normalized by HPC theta power change and the estimated on/off target effects. (E) The change of SuM/MM theta power relative to HPC changes in a coronal plane collapsed through five anterior-posterior planes around the septal region. Warmer colors indicate more “sensitivity” (i.e., relatively more SuM/MM theta power decrease compared to HPC) to MS-inactivation. (F) Correlation between the change of SuM/MM dominant theta frequency and the recording position in the anterior-posterior axis. (G) Correlation between the change of SuM/MM dominant theta frequency and the estimated on/off target effects. (H) Changes in SuM/MM theta dominant frequency in response to MS-inactivation mapped in coronal planes across five anterior-posterior points. Colors indicate the magnitude and direction of dominant theta frequency changes seen in the SuM/MM comparing post- and pre-MS-inactivation. HPC, hippocampus; MS, medial septum; SuM, supramammillary nucleus; MM, mammillary bodies; AP anterior-posterior.