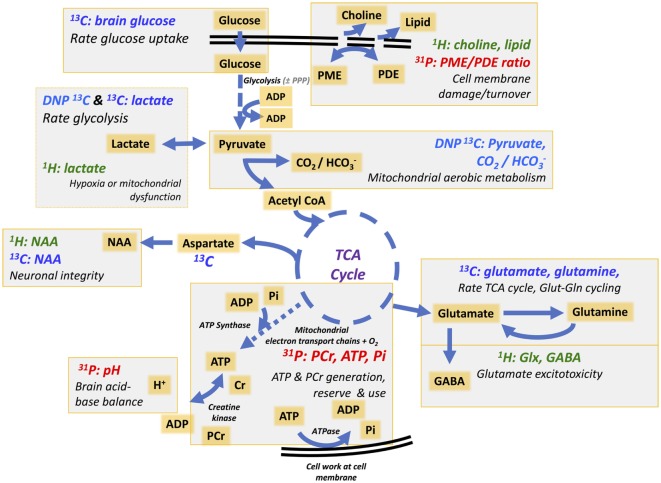
Figure 5.
Simplified schematic of different metabolites and processes in the brain that can be interrogated using 1H MRS, 31P MRS, 13C MRS, and DNP 13C MRS. 1H and 31P MRS show endogenous metabolites; 13C MRS requires exogenous 13C-enriched substrate, while for DNP 13C MRS the exogenous 13C-enriched substrate is hyperpolarized before administration, transiently boosting 13C signal. Pathways include uptake of glucose that is metabolized via glycolysis in the cytosol [with a low yield of ATP per mole of glucose consumed] producing pyruvate. Pyruvate can enter mitochondria where it is converted into acetyl-CoA that enters the TCA cycle. Pyruvate remaining in the cytosol can be converted into lactate, simultaneously recycling NADH into NAD+ allowing glycolysis to continue. The rate of glucose uptake and glycolysis can be interrogated with 13C MRS (glucose and lactate appearance) whereas the relative flux of “anaerobic” metabolism vs. aerobic mitochondrial metabolism can be measured with DNP 13C MRS (lactate vs. ) and 1H MRS (lactate). The TCA cycle drives the mitochondrial electron transport chain for high-yield ATP synthesis. The rate of the TCA cycle can be calculated by the rate of appearance of 13C labeled glutamate (Glu) (13C MRS) and ATP produced measured with 31P MRS (γ-ATP, β-ATP, and Pi). Neuronal integrity and mitochondrial function can be measured indirectly by detection of NAA with 1H MRS (and 13C MRS). Neuronal–glial coupling is represented by Glu–glutamine (Gln) cycling detected by 13C MRS, whereas total combined Glu and Gln that may be raised in pathological excitotoxicity can be measured with 1H MRS. Cell membrane integrity and damage and turnover may be represented by 1H MRS (choline and lipid) and 31P MRS (PME/PDE ratio), which also can detect the balance and consumption of high-energy phosphates (ATP, PCr, and Pi). Further details of the above, and other MRS-detectable molecules (including creatine, myoinositol, glycogen, and nicotinamide-adenine dinucleotides), can be found in the text. Abbreviations: ADP, adenosine diphosphate; ATP, adenosine triphosphate; Cr, creatine; DNP, dissolution dynamic nuclear polarization; GABA, gamma-aminobutyric acid; NAA, N-acetylaspartate; MRS, magnetic resonance spectroscopy; NAD+, nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide oxidized form; NADH, nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide reduced form; PCr, phosphocreatine; PDE, phosphodiester; PME, phosphomonoester; Pi, inorganic phosphate; PPP, pentose phosphate pathway; TCA, tricarboxylic acid.