Figure 2.
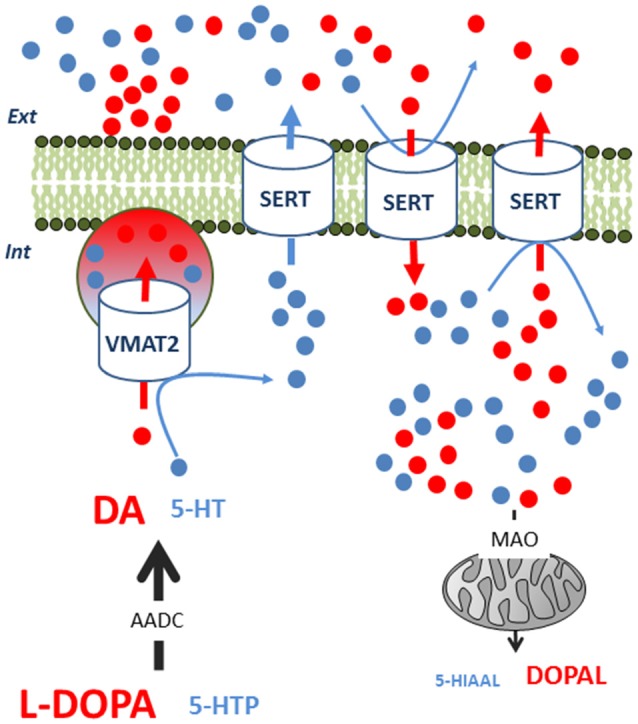
Competition between L-DOPA-derived dopamine (DA) and serotonin (5-HT) inside 5-HT neurons. L-DOPA competes with 5-HTP for AADC to synthesize DA and 5-HT, respectively. DA competes with 5-HT in terms of VMAT2-mediated packaging of exocytotic vesicles. In consequence, intracellular 5-HT levels can transiently rise and 5-HT can exit the neuron via SERT in a non-exocytotic manner. This 5-HT output can only be observed under specific conditions, as L-DOPA-derived DA can also alter the function of SERT. First, extracellular DA can undergo reuptake by SERT, reducing the 5-HT flow through this transporter. Second, intracellular DA can also enter the neuron through the SERT, impairing the output of 5-HT. In the cytoplasm, MAO can more efficiently degrade DA than 5-HT, increasing oxidative metabolism and aldehyde derivates. These biochemical events occur with no modification of the firing rate of 5-HT neurons. AADC, amino acid decarboxylase, L-DOPA, 3,4-Dihydroxyphenylacetaldehyde; MAO, monoamine oxidase; SERT, serotonin transporter; VMAT2, monoamine vesicular transporter; 5-HIAAL, 5-hydroxyindole acetaldehyde; 5-HTP, 5-hydroxytryptophan.
