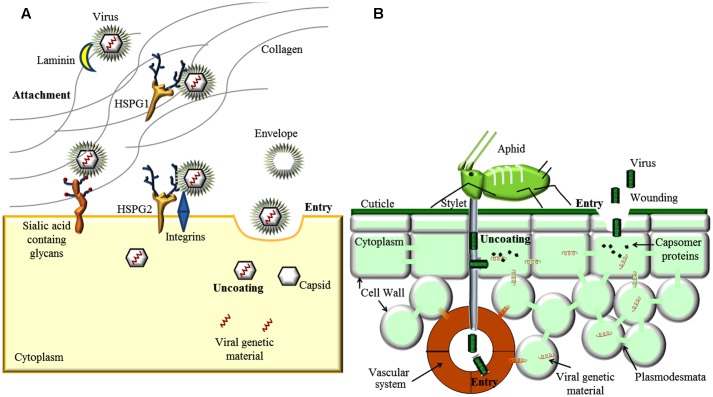
FIGURE 1.
Involvement of Extracellular matrix and Cell Wall (CW) in virus entry. (A) In animal virus entry, the virus can bind to extracellular matrix (ECM) receptors, like Laminin, Heparan Sulfate Proteo Glycan 1 (HSPG 1) and integrins. Viruses can interact with secondary binding sites (HSPG 2 or sialic acid-containing glycans) present on the cell surface. Interaction with cell surface receptor can induce conformational triggering endocytosis. (B) Plant viruses can enter host cells and get in contact with the cytoplasm only via feeding of invertebrate vectors, e.g., aphids, or trough mechanical wounding involving partial destruction of the CW. Once inside the cell cytoplasm, both animal and plant viruses are uncoated and replicated following similar routes.