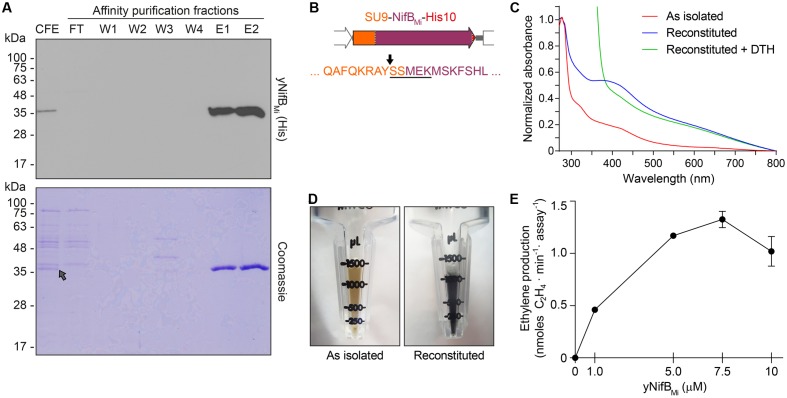
FIGURE 4.
Purification and biochemical properties of yNifBMi. (A) SDS-PAGE and Western blot analysis of yNifBMi purification. CFE, 65°C heated SB10Y cell-free extract; FT, affinity chromatography flow through; W1-W4 and E1-E2, affinity chromatography wash and elution fractions containing increasing concentrations of imidazole (see Materials and Methods for details). Grey arrow in the Coomassie stained panel points to the position of yNifBMi in the gel. (B) SU9 processing site (black arrow) of yNifBMi. Underlined sequence indicates the N-terminal amino acids of yNifBMi identified by Edman degradation. (C) UV-visible spectra of as isolated, reconstituted, and dithionite (DTH)-reduced reconstituted yNifBMi. (D) Typical color of as isolated and reconstituted yNifBMi purified preparations. (E) Titration of FeMo-co synthesis and nitrogenase reconstitution assay with yNifBMi. The indicated concentrations of yNifBMi monomer were used. NifB activity was determined by acetylene reduction assay of reconstituted NifDK from ΔnifB A. vinelandii UW140 cell-free extracts. Data represent mean ± standard deviation (n = 2) at each yNifBMi concentration.