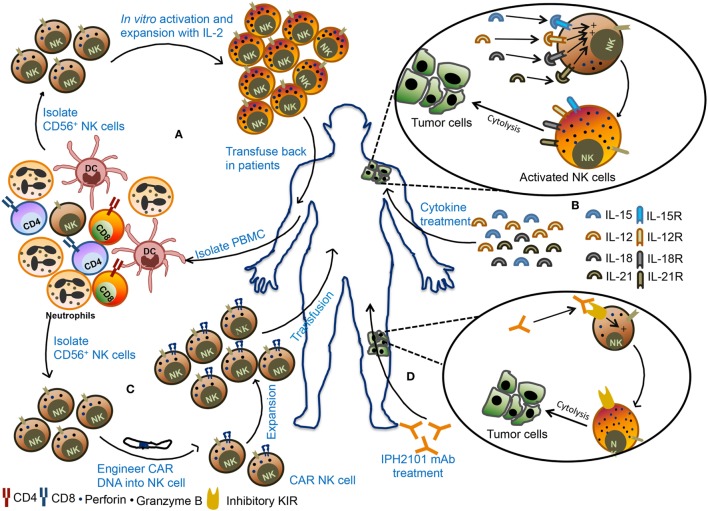
Figure 5.
Various natural killer (NK) cell-based immunotherapy approaches. (A) In adoptive cellular therapy, NK cells are freshly isolated from peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) from the patient. These NK cells are ex vivo activated and expanded and then transfused back into the patient. (B) In the second strategy, patients are treated with recombinant cytokines such as IL-2, IL-15, IL-12, or IL-18. These cytokines promote activation and proliferation of NK cells in the body leading to better antitumor immunity. (C) In the third strategy, NK cells are engineered to express chimeric antigen receptor (CAR), followed by expansion of these CAR NK cells, and transfused back into the patient. (D) In monoclonal antibody (mAb)-based treatment, patients are treated with IPH2101, a blocking mAb against inhibitory receptors and these mAb can promote NK cells activity in the tumor microenvironment and restrict tumor growth.