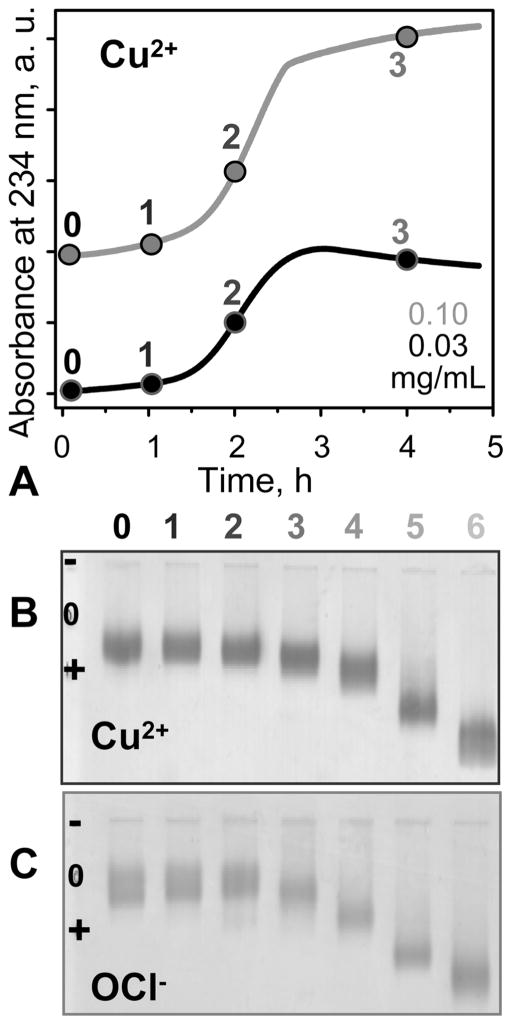
Figure 2.
VLDL oxidation to various stages by Cu2+ or OCl−. (A, B) VLDL in EDTA-free standard buffer (5 mM sodium phosphate, 0.02% NaN3, pH 7.6) were incubated at 37 °C with 5 μM CuSO4 for up to 48 h. (A) The time course of VLDL oxidation by copper was monitored by absorbance at 234 nm for conjugated diene formation. The absorbance is presented for the first 5 h of incubation; no additional changes were observed after further incubation. (B) Agarose gel electrophoresis monitors changes in electronegativity resulting from oxidative Lys modifications and formation of free fatty acids (FFA). Numbers in (A) and (B) correspond to incubation times of 1 h (1), 2 h (2), 4 h (3), 12 h (4), 24 h (5), and 48 h (6); 0 stands for intact VLDL. (C) VLDL in standard buffer (5 mM sodium phosphate, 0.02% NaN3, 0.25 mM EDTA, pH 7.6) was oxidized to various stages by incubating for 12 h at 37 °C in NaOCl solutions of 0.045 (1), 0.2 (2), 0.5 (3), 0.8 (4), 1.0 (5), and 5.0 mM (6) concentration. VLDL protein concentrations are 0.03 (black) or 0.1 mg/mL (gray) in (A) and 0.5 mg/mL in (B) and (C).