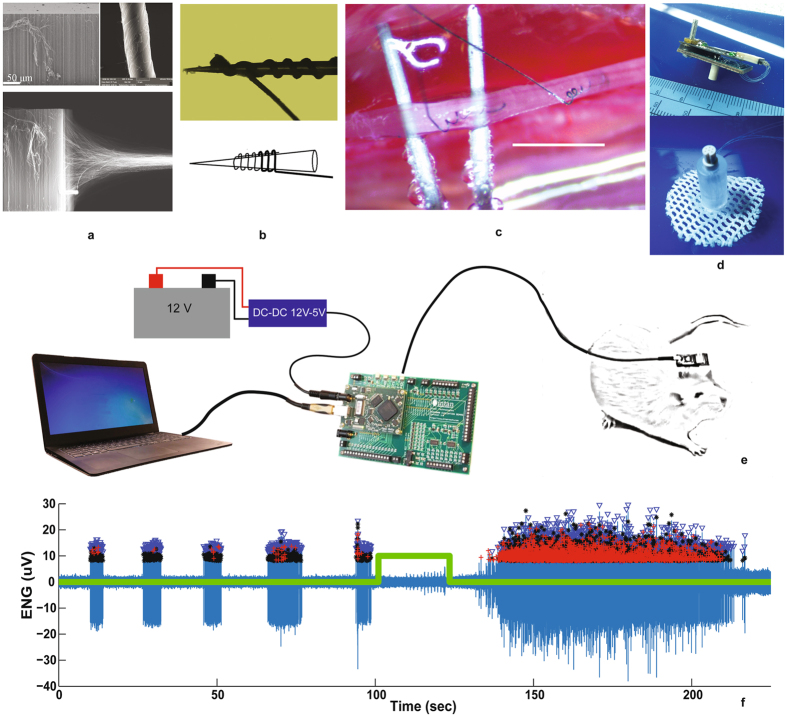
Figure 1.
Chronic autonomic nerve recording using CNT yarns. (a) CNT forest being pulled and spun to form CNT yarns that are 10 microns in diameter. (b) CNT yarns wound around the tip of a Tungsten microneedle used to implant the yarn into the nerve. (c) Two CNT yarns implanted in the rat vagus nerve separated by ~2 mm for differential recording of the neural activity [scale bar = 2 mm]. (d) Percutaneous plug with electrical connector that directly mates to the neural amplifier recording circuit board for signal amplification, filtering and acquisition. (e) Schematic of the complete recording assembly from the CNT yarn implants, lead wire connections, percutaneous plug, the external neural recording amplifier board and evaluation system board for data storage. (f) Post processed, spontaneous neural activity from the vagus nerve, 16-weeks post implant (blue). Trigger signal (green trace) indicating the hypoxia event administered to the anesthetized rat. Also shown are the markers for each identified neural spike and cluster grouping for activity identification and classification. Evaluation system board photo used with permission courtesy of Intan Technologies, LLC.