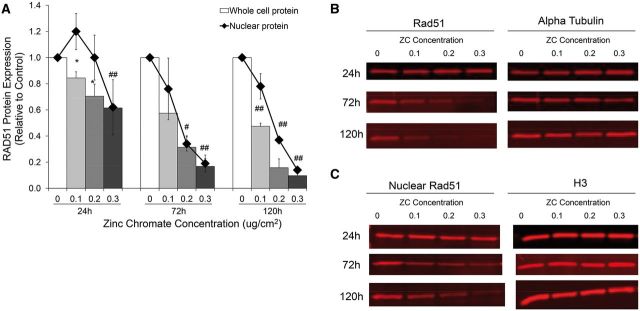
FIG. 1.
Prolonged exposure to zinc chromate decreases whole cell and nuclear Rad51 protein expression in a time and dose dependent manner. A, This figure shows zinc chromate induced a dose-dependent decrease in whole cell Rad51 at all time points. Zinc chromate exposure caused an increase in nuclear Rad51 protein at 24h exposure, but a dose-dependent decrease in nuclear Rad51 protein at 72 and 120 h exposure. Whole cell protein data represent an average of 3 experiments. Error bars = SEM. All doses except for 0.1 μg/cm2 at 72 h exposure were significantly different from controls (*P < .05; # P < .005; ## P < .001). Nuclear protein data represent an average of 3 experiments. Nuclear protein levels were significantly lower than controls after 0.2 μg/cm2 zinc chromate at 72 and 120 h and 0.3 μg/cm2 at all time points (P < .01). B, Representative images of whole cell Rad51 western blots. C, Representative images of nuclear Rad51 western blots.