Figure 5. PIM overexpression correlates with an immune system-dependent genes signature in human breast, endometrium and ovary tumors.
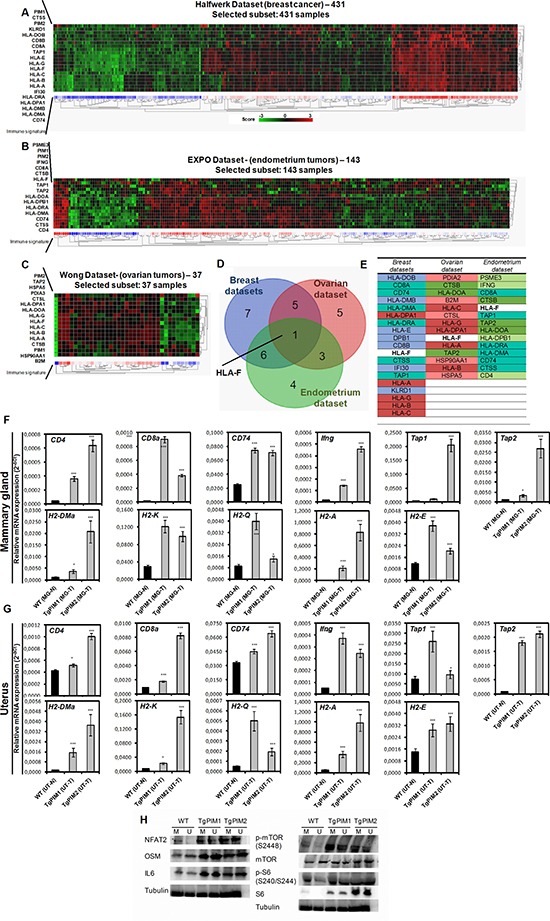
(A) The figure shows a heat map comparing immunology-related genes with PIM1 and PIM2 (See Supplementary Table 3) in breast tumors (Halfwerk dataset, R2). Heat map shows a clear correlation of PIM1 and PIM2 with the expression of antigen presentation genes. (B) The figure shows a heat map comparing immunology-related genes with PIM1 and PIM2 (See Supplementary Table 4) in endometrial tumors (EXPO dataset, R2). Heat map shows a clear correlation of PIM1 and PIM2 with the expression of antigen presentation genes. (C) The figure shows a heat map comparing immunology-related genes with PIM1 and PIM2 (See Supplementary Table 5) in ovarian tumors (Wong dataset, R2). Heat map shows a clear correlation of PIM1 and PIM2 with the expression of antigen presentation genes. (D) A Venn diagram showing the number of immune system-dependent genes that correlated with PIM1 and PIM2 overexpression in Breast, endometrial and ovary tumors. (E) A list of system-dependent genes in Breast, endometrial and ovary tumors that correlated with both PIM1 and PIM2 overexpression (common) and that was unique to each tumor type. (F, G) Pro-inflammatory microenvironment PIM-dependent characterization by qPCR. The figure shows a number of immune system-dependent genes that were correlated with PIM overexpression in breast, endometrium and ovarian datasets: CD4, CD8a, CD74, Ifng, Tap1 and Tap2; and mouse Major Histocompatibility Complex markers (H2 complex). We decided to focus on the ones which has a mouse ortholog: HLA-DMA (H2-DMa), HLA-DRA (H2-A), HLA-DPB1 (CD74), and also H2-K (classical MHC class I), H2-Q (non-classical MHC class I), H2-E (classical MHC class II). They were measured by qRT-PCR of mammary gland of WT mice with non-proliferative status (MG-N) and carcinoma grades (MG-T) in both transgenic models (F), and the same way in uterus (UT-N, normal; and UT-T, carcinoma) (G). (H) The overexpression levels of the human transgenes PIM1 or PIM2 in the models causes an increase in the expression of NFAT and NFAT effectors (OSM and IL6), as well as the phosphorylation of mTOR. The p-value was obtained using a one-tailed student's t-test. (*p < 0.05), (**p < 0.01), and (***p < 0.001).
