Figure 4. The roles of regulating brain miR-144 in cognitive deficits of TBI rats.
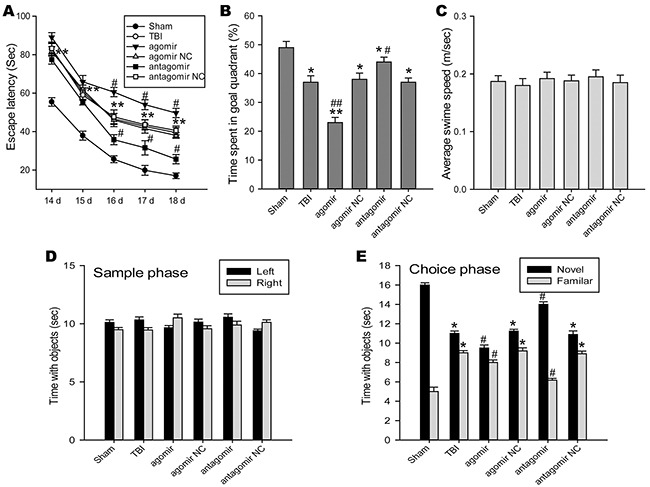
The cognitive function was evaluated by morris water mass (MWM) test including the spatial acquisition trial and the probe trial at 14 -18 d post-TBI, as well as novel object recognition (NOR) test at 18 d post-injury. (A) MWM performance as measured by the latency to find the hidden platform in the spatial acquisition trial (n=6). miR-144 antagomir treated group has significantly shorter latencies to reach the goal platform as compared to the TBI group. (B) Percentages of time spent in the goal quadrant during the probe trial (n=6). The rats administrated with miR-144 antagomir had significantly better retention of the platform location compared with rats suffered from TBI. (C) The overall average swim speed during test duration in different groups (n=6). (D-E) Intracerebroventricular injection of miR-144 antagomir improves retention memory using the NOR test at 18 d post-TBI (n=6). Following 24 h after the sample phase, the time spent with the novel object sand familiar objects during the choice phase was recorded. The data are represented as mean ± SD. *P< 0.05, *P< 0.01 versus the sham group, #P< 0.05, ##P< 0.01 versus the TBI group.
