Figure 4. Dinaciclib (SCH) induces apoptosis in various MM cells in association with Pol II inhibition and Mcl-1 downregulation.
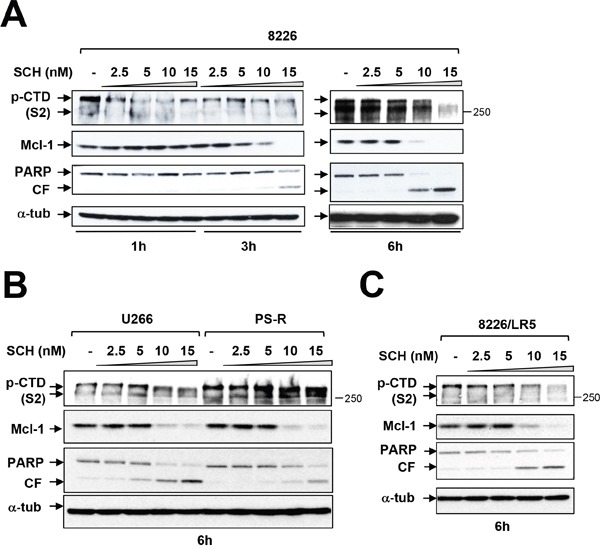
(A) Logarithmically growing RPMI8226 cells were exposed to 2.5 nM to 15 nM dinaciclib (SCH) for 1, 3, and 6 hr, after which protein extracts were obtained and subjected to immunoblot analysis to monitor the expression of phosphorylated forms (serine-2 and 5, CTD) of RNA pol II, Mcl-1, and PARP as described previously. Lanes were loaded with 30 μg of protein; α-tubulin controls were assayed to ensure equivalent loading and transfer. Duplicate experiments yielded equivalent results. CF = cleavage fragment. (B) U266 and PS-R (bortezomib-resistant U266) cells were exposed to 2.5 nM to 15 nM SCH for 6 hr. After treatments, immunoblotting analysis was carried out to monitor phosphorylated form (serine-2, CTD) of RNA pol II, Mcl-1, and PARP cleavage fragment (CF). (C) RPMI8226/LR5 (melphalan-resistant) cells were treated the same as B. for 6 hr. After treatments, immunoblotting analysis was carried out to monitor the phosphorylated (serine-2, CTD) RNA pol II, Mcl-1, and PARP cleavage (CF). Each lane was loaded with 30 μg of protein; α-tubulin controls were assayed to ensure equivalent loading and transfer.
