Figure 5. Genetic or pharmacologic CDK9 inhibition promotes proteasome inhibitor (PI) lethality in bortezomib-resistant MM cells.
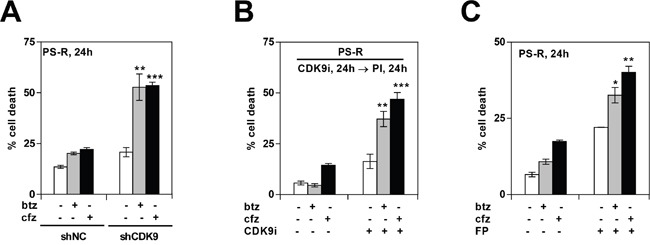
(A) PS-R (bortezomib-resistant U266) cells were stably transfected with constructs encoding shRNA targeting CDK9 (shCDK9) or scrambled sequence (shNC). Cells were then treated with 15 nM bortezomib (btz) or 25 nM carfilzomib (cfz) for 24 hr, after which cell death was analyzed by flow cytometry after staining with 7-AAD. Significantly greater than values for control cells: ** = P < 0.01; *** = P < 0.001. (B) PS-R cells were treated with CDK9i (15 μM) for 24 hr, followed by exposure to 15 nM btz or 25 nM cfz for an additional 24 hr. Cell death (7-AAD) was analyzed by flow cytometry. ** = P < 0.01; *** = P < 0.001. (C) PS-R cells were treated with btz (15 nM) or cfz (25 nM) with or without alvocidib (FP; 150 nM) for 24 hr, and then analyzed by flow cytometry to determine the percentage of apoptotic cells. Significantly greater than control; * = P < 0.05; ** = P < 0.01.
