Figure 6.
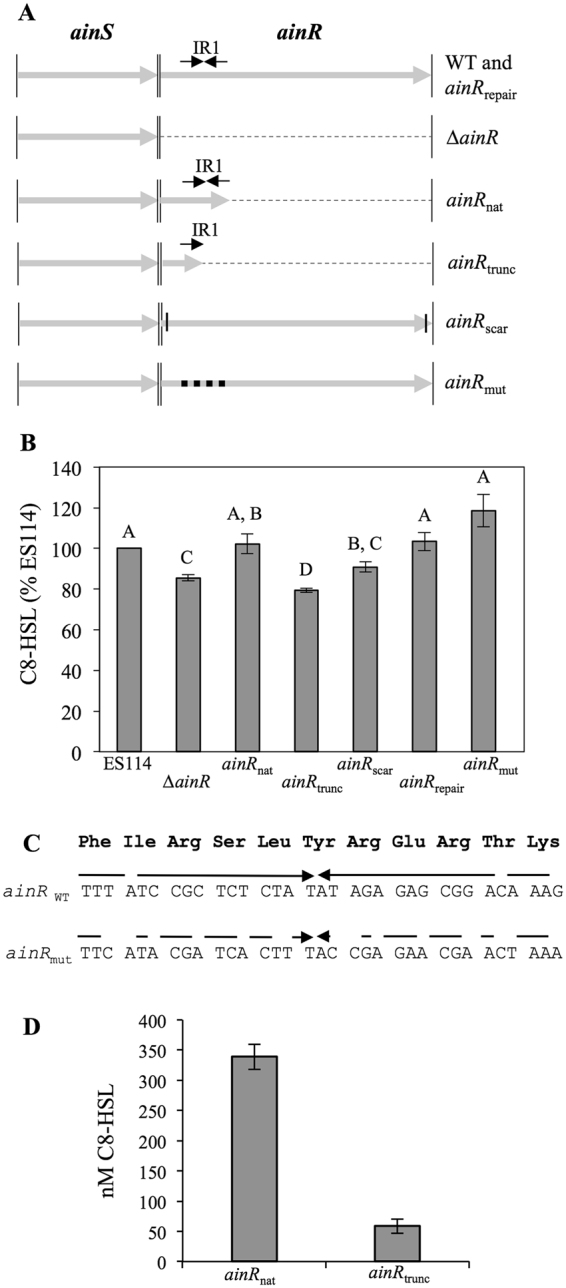
Effects of ainR sequence on C8-HSL accumulation. Panel A: Illustration of ainR alleles in this study. The ainS and ainR genes are shown as grey arrows delineated by thin vertical lines. Dashed lines correspond to deletions in ainR. Each repeat in IR1 is shown as a black arrow, and in ainR mut the IR is altered to scramble the inverted repeat without changing the amino acid sequence. In ainR scar, short horizontal lines near the ainR termini indicate 6-bp insertions from restriction enzyme sites. Panel B: C8-HSL accumulation in cultures of strains ES114, JHK003 (∆ainR), JHK055 (ainR trunc), JHK056 (ainR nat), JHK115 (ainR scar), JHK119 (ainR repair), JHK120 (ainR mut) grown with shaking in SWTO medium to an OD595 ~1.5. Letters indicate significant differences (P < 0.05) in ANOVA test. Panel C: Alignment of IR1 region in wild type (ainRWT)and the targeted mutant ainR mut showing conservation of amino acids encoded and increased number of mismatches in the inverted repeat, which are depicted as gaps in arrows. Panel D: C8-HSL accumulation in cultures of E. coli MG1655 carrying the ainR nat and ainR trunc alleles on pHK103 and pHK102, respectively, grown shaking in LB to OD595 ~1.5. Bars indicate standard error (n = 2).
