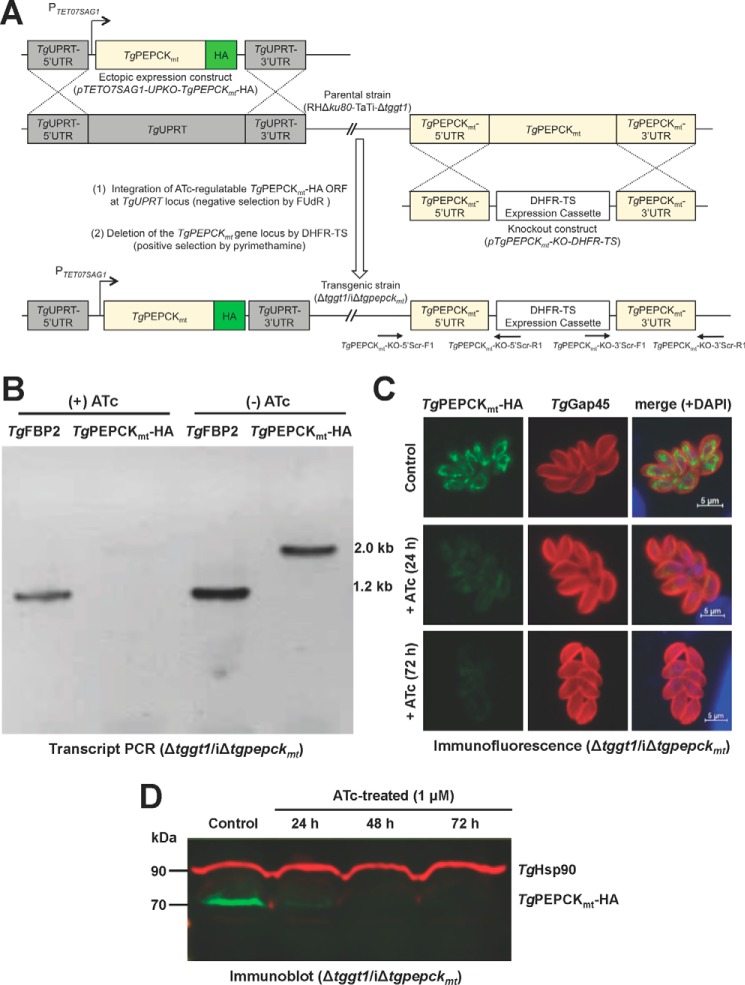
Figure 4.
Conditional mutagenesis enables a tetracycline-regulated knockdown of TgPEPCKmt in glycolysis-impaired tachyzoites. A, scheme for generating a tetracycline-inducible mutant of TgPEPCKmt (iΔtgpepckmt) in a GT1 knock-out strain with impaired glycolysis (RHΔku80-TaTi-Δtggt1). In the first step, an ATc-repressible ORF of TgPEPCKmt-HA was integrated at the TgUPRT locus by FUdR selection, and then the TgPEPCKmt gene was replaced by DHFR-TS. The eventual Δtggt1/iΔtgpepckmt mutant was identified by genomic PCR using 5′ and 3′-crossover-specific primers (TgPEPCKmt-KO-5′Scr-F1/R1 and TgPEPCKmt-KO-3′Scr-F1/R1). B, PCR confirming the regulation of TgPEPCKmt transcript by ATc in the Δtggt1/iΔtgpepckmt mutant. Total parasite RNA was used to amplify TgPEPCKmt-HA and TgFBP2 (control for RNA integrity) using ORF-specific primers. C, immunostaining of the Δtggt1/iΔtgpepckmt strain showing ATc regulation of TgPEPCKmt-HA protein. The untreated control and drug-treated parasites were stained using α-HA and α-TgGap45 (a marker of inner membrane complex) antibodies. D, immunoblot depicting the ATc-mediated repression of TgPEPCKmt-HA in the conditional mutant. Parasites (107) were subjected to immunoblot analyses using α-HA and TgHsp90 (loading control) antibodies.