Figure 8.
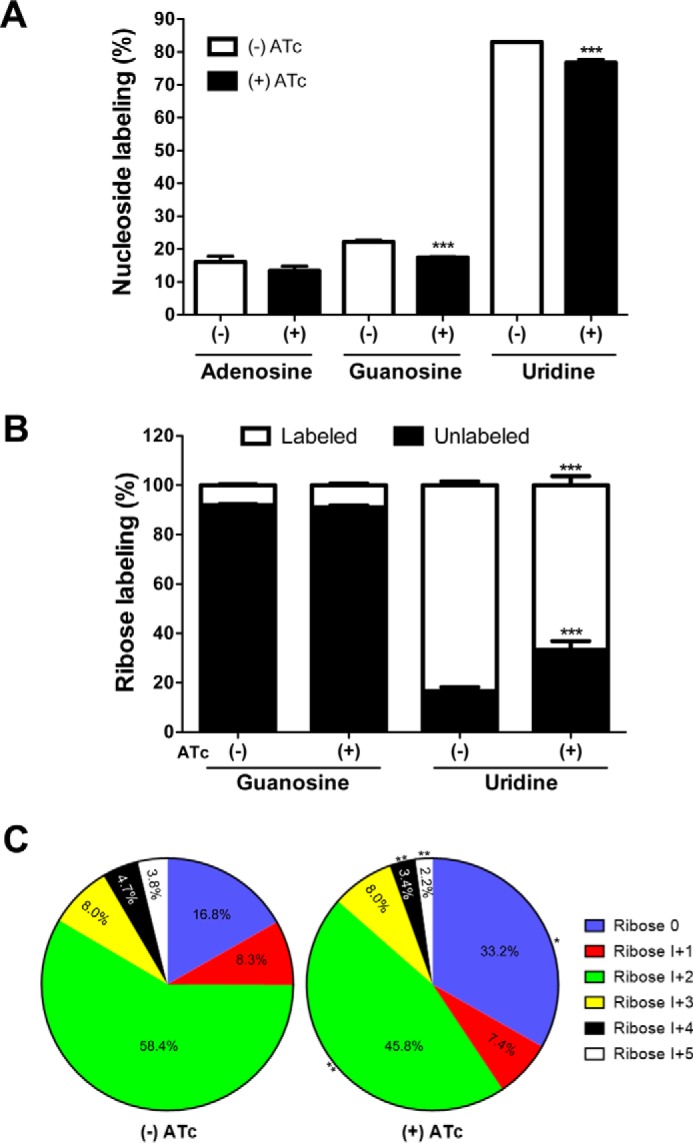
Glutamine-derived carbon is utilized for synthesis of RNA in the Δtggt1/iΔtgpepckmt strain. A, inclusion of 13C in adenosine, guanosine, and uridine nucleosides of RNA labeled with [U-13C]glutamine (12 h, 37 °C, 5% CO2) in the presence or absence of ATc. The figure shows general labeling based on the total ion current data, which do not discriminate between the label in ribose or base. B, stable isotope labeling of ribose in nucleosides, as deduced by MS/MS. The labeling of ribose in adenosine was undetectable, and in guanosine, it was >10%. The minor labeling of purines appears to be a consequence of isotope inclusion in the base, probably through glycine and CO2 derived from glutamine's usage through the TCA cycle. C, fractional abundance of the 13C atoms in all isotopomers of the ribose moiety of uridine. Percentage fractions of the unlabeled (Ribose 0) and labeled isotopomers (I+1 to I+5) are displayed for the drug-treated and control samples. Statistical analysis was done using Student's t test (*, p < 0.05; **, p < 0.01; ***, p < 0.001; mean ± S.E. (error bars), n = 4 assays).
