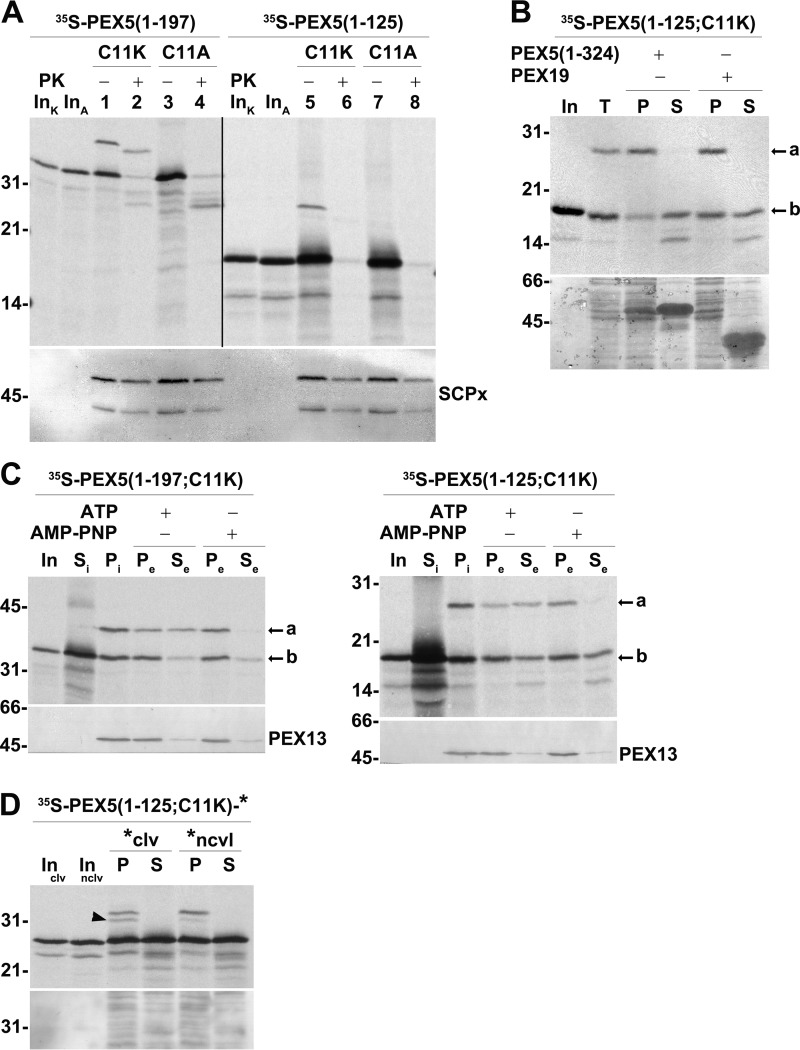
Figure 6.
DTM-bound PEX5(1–125;C11K/A) is accessible to PK. A, PEX5(1–125;C11K) is correctly monoubiquitinated but does not acquire a PK-protected status. A primed PNS (see “Experimental procedures”) was used in AMP-PNP-supplemented in vitro assays programmed with radiolabeled PEX5(1–197;C11K) (lanes 1 and 2; C11K), PEX5(1–197;C11A) (lanes 3 and 4; C11A), PEX5(1–125;C11K) (lanes 5 and 6; C11K), or PEX5(1–125;C11A) (lanes 7 and 8; C11A). One-half of each reaction was treated with PK as indicated. Organelle fractions were analyzed by SDS-PAGE/Western blotting/autoradiography. The autoradiograph (upper panel) and the corresponding nitrocellulose membrane probed with an antibody directed to sterol carrier protein x (SCPx; lower panel) to assess intactness of peroxisomes (86) are shown. The exposure time of the PEX5(1–125;C11K/A) panel was 4-fold longer than that of PEX5(1–197;C11K/A) to obtain similar intensities of the ubiquitinated species. Note that PEX5(1–197;C11K/A) and PEX5(1–125;C11K/A) have the same number of methionines. Lanes InK and InA, RRL containing the C11K and C11A versions of the indicated 35S-proteins, respectively. B, Ub-PEX5(1–125;C11K), but not PEX5(1–125;C11K), is tightly bound to organelles. Radiolabeled PEX5(1–125;C11K) was incubated with a primed PNS in AMP-PNP-containing import buffer for 30 min at 37 °C. The organelles were then recovered by centrifugation, resuspended in import buffer, and divided into three tubes. One tube was kept on ice (lane T), and the other two tubes were incubated for 15 min at 37 °C in the presence of 10 μg of either recombinant PEX5(1–324) or PEX19 as indicated. Organelles (P) and the corresponding supernatants (S) were separated by centrifugation and analyzed by SDS-PAGE/autoradiography. Lane In, RRL containing the radiolabeled protein. The autoradiograph (upper panel) and a portion of the corresponding Ponceau S-stained membrane (lower panel) are shown. C, Ub-PEX5(1–125;C11K) is a substrate for the REM. Radiolabeled PEX5(1–197;C11K) (left panels) or PEX5(1–125;C11K) (right panels) was incubated with a primed PNS in import buffer supplemented with ubiquitin aldehyde and AMP-PNP. The reactions were then centrifuged to separate supernatant fraction (Si) from organelles (Pi). The organelles were resuspended in an ATP- or AMP-PNP-containing import buffer and further incubated for 15 min at 37 °C. The organelle suspensions were again centrifuged to obtain a supernatant (Se) and an organelle pellet (Pe). Samples were analyzed by SDS-PAGE/Western blotting/autoradiography. The autoradiographs (upper panels) and the behavior of endogenous PEX13 (lower panels) are shown. Si, equivalent to 50 μg of PNS; Pi, Pe, and Se, equivalent to 600 μg of PNS. Lanes In, RRL containing the radiolabeled protein. In B and C, a and b indicate monoubiquitinated and non-ubiquitinated PEX5 species, respectively. D, radiolabeled PEX5(1–125;C11K)-clv is partially processed in the PNS-based in vitro assay. Radiolabeled PEX5(1–125;C11K)-clv and PEX5(1–125;C11K)-nclv were subjected to PNS-based in vitro assays in the presence of AMP-PNP for 60 min. The reactions were then centrifuged to separate organelles (lanes P) from soluble proteins (lanes S). Organelles and soluble fractions from 600 and 100 μg of PNS, respectively, were subjected to SDS-PAGE/Western blotting/autoradiography. Lanes Inclv and Innclv, RRL containing the indicated 35S-labeled proteins. The autoradiograph (upper panel) and the corresponding Ponceau S-stained membrane (lower panel) are shown. The cleaved species is indicated by an arrowhead. Numbers to the left indicate the molecular mass (kDa) of protein standards.