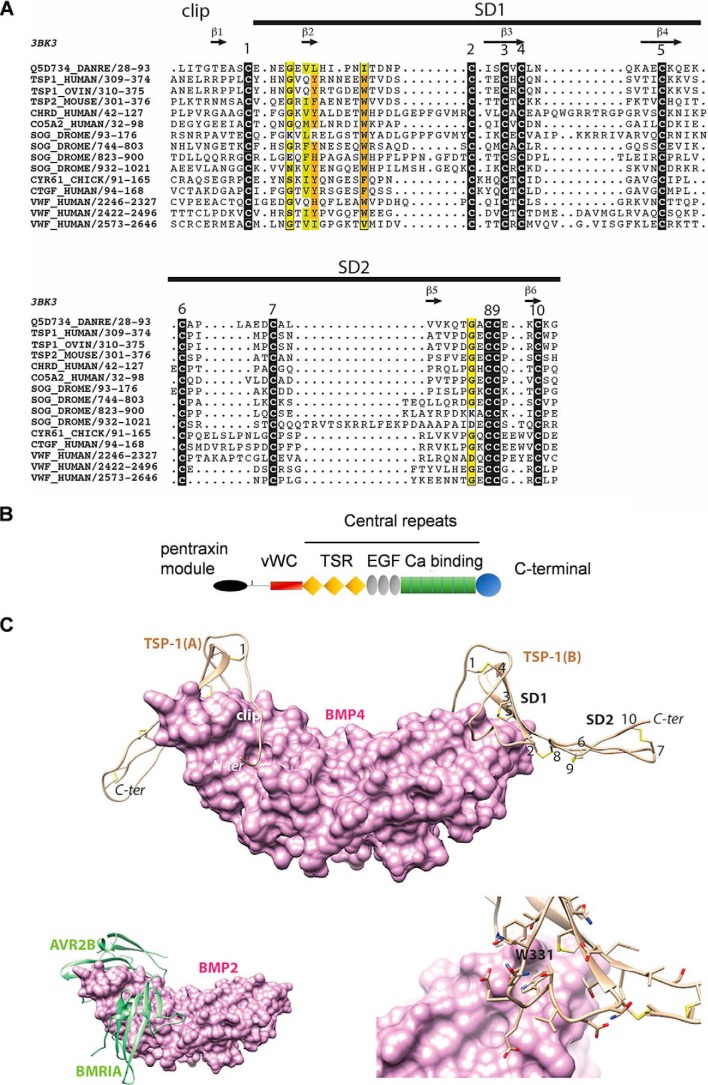
Figure 7.
A, multiple sequence alignment of the VWC domain of TSP-1 with other VWC domains from the chordin family, including that of CV-2 (Q5D734_DANRE) whose 3D structure is known (PDB ID 3bk3). Black boxes indicate highly conserved cysteine residues. Observed secondary structures and disulfide bonds are reported above and below the alignment, respectively. Sequences are designated with their UniProt identifiers. B, schematic diagram of domain architecture of TSP-1 (modified from Ref. 43) vWC = vWC domain; TSR = thrombospondin type 1 domain repeats; EGF = EGF like domain repeats; Ca binding = calcium-binding type 3 repeats. C, top, model of the 3D structure of the TSP-1 VWC domain (ribbon representation) in complex with BMP-4 (surface representation). The three subdomains (clip, SD1, and SD2) are shown together with the five disulfide bridges (numbering is as depicted in Fig. 1). The model was built based on the 3D structure of CV-2 in complex with BMP-2 (PDB ID 3BK3) (34) and on the alignment shown in Fig. 1. Bottom left, experimental structure of BMP-2 bound to its high-affinity type I receptor BMPR-IA and its low-affinity type II receptor ActR-IIB (PDB ID 2H62) (34) in order to show the overlap with the VWC domain-binding sites. Bottom right, focus on the Trp-331 amino acid, fitting with a groove at the surface of BMP-4.