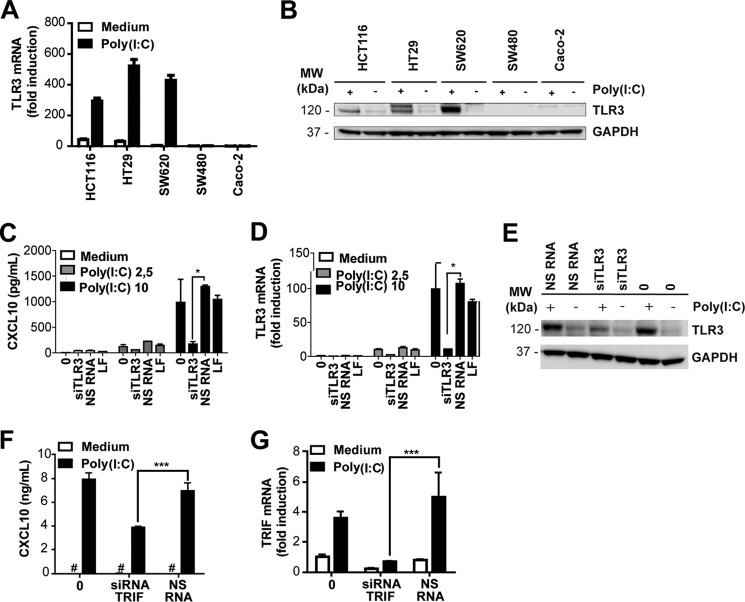
Figure 2.
Poly(I:C)-responsive IECs up-regulate TLR3 expression and induce CXCL10 in a TLR3- and TRIF-dependent manner. A, TLR3 mRNA expression in SW620, SW480, HT29, HCT116, and Caco-2 cells treated with medium or poly(I:C) (5 μg/ml) for 24 h before TLR3 expression was determined by qPCR. GAPDH served as an internal control. The results show mean induction of triplicates ± S.D. relative to untreated Caco-2 cells and are representative of three independent experiments. B, TLR3 protein expression in SW620, SW480, HT29, HCT116, and Caco-2 cells left untreated (−) or treated with poly(I:C) (2.5 μg/ml) (+) for 24 h. Western blots were stained with anti-TLR3 (top) or GAPDH as a loading control (bottom). MW, molecular weight. C and D, CXCL10 release (C) and TLR3 mRNA expression (D) in SW620 cells left untreated (0), transfected with TLR3 siRNA (siRNA TLR3.5, 5 nm) or NS RNA (5 nm) or treated with the transfection reagent LF alone for 28 h prior to stimulation with poly(I:C) (2.5 or 10 μg/ml) for 20 h. CXCL10 release in the supernatant was assessed by ELISA. TLR3 mRNA expression in the lysates of the treated SW620 cells was determined by qPCR using GAPDH as an internal control. Results show mean ± S.D. of triplicates and are representative of three independent experiments. E, Western blots showing TLR3 (top) and GAPDH (bottom) expression in SW620 cells transfected with TLR3 siRNA (10 nm), NS RNA (10 nm), or transfection reagent (0) alone for 24 h prior to stimulation with poly(I:C) (2.5 μg/ml) for 24 h. F and G, CXCL10 production (F) and TRIF mRNA expression (G) in HT29 cells left untreated (0) or treated with siRNA against TRIF (20, 15, 10, or 5 nm) or with NS RNA (10 nm) for 24 h prior to stimulation with poly(I:C) (5 μg/ml) for 20 h. CXCL10 content in cell supernatant was assessed by ELISA, whereas silencing of TRIF was confirmed by assessing TRIF mRNA by qPCR using GAPDH as a reference control. The results show mean ± S.D. of triplicates and are representative of two independent experiments. ***, p < 0.001 versus NS RNA (one-way ANOVA, Holm-Sidak multiple comparisons).