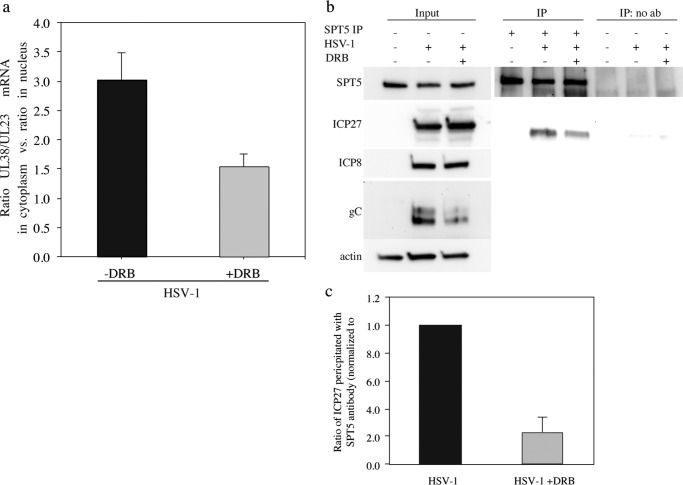
Figure 7.
DRB reduces cytoplasmic accumulation of HSV-1 mRNA and the amount of ICP27 co-immunoprecipitated with SPT5. a, 1BR.3.N cells were infected with HSV-1 at an m.o.i. of 1. RNA was isolated from nuclear and cytoplasmic fractions obtained by subcellular fractionation. The ratio between UL38 and UL23 mRNA in the cytoplasm and the nucleus was determined by multiplex RT-qPCR at 19 h.p.i. in four independent experiments. The results are displayed as the mean value of the quotient between cytoplasmic and nuclear ratios in the presence (black) or absence of 25 μm DRB (gray), and the error bars indicate standard deviation. The statistical significance determined by unpaired two-tailed Student's t test with unequal variance was p = 0.0074. b, immunoblot from an anti-SPT5 immunoprecipitation experiment using extracts from HSV-1-infected HeLa cells. The cells were infected at an m.o.i. of 10 and treated either with 25 μm DRB or with DMSO at 1 h.p.i. At 17 h.p.i., the cells were harvested and submitted to anti-SPT5 immunoprecipitations. c, quantification of three independent immunoprecipitation experiments. The ratios between the measured amounts of ICP27 and SPT5 from experiments performed in the presence or absence of DRB were calculated. The ratios obtained in the absence of DRB were used for normalization. The error bars indicate standard deviation.