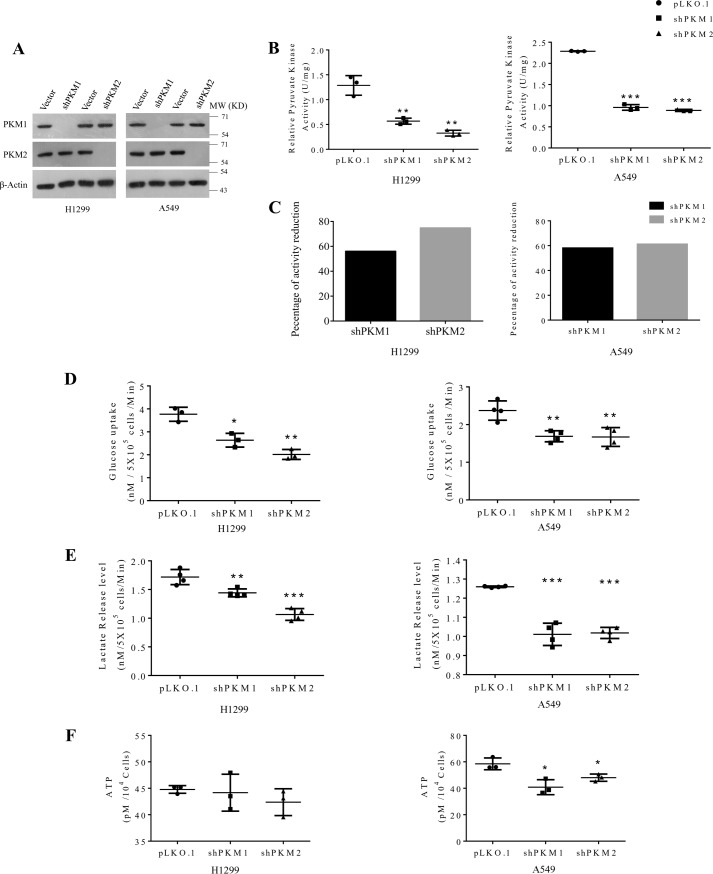
Figure 5.
Knockdown of PKM1 or PKM2 differentially affects the metabolism of human lung cancer cells H1299 and A549. A, immunoblots to validate the stable knockdown of PKM1 and PKM2 expression in H1299 (left panel) and A549 (right panel) cells, transduced with vector control (pLKO.1), shPKM1, or shPKM2. B, relative pyruvate kinase enzyme activity from protein lysates of H1299 (left panel) and A549 (right panel) cells stably transduced with control vector (pLKO.1), shPKM1, or shPKM2; with statistical analysis (where n ≥ 3; mean ± S.D.), and the level of significance was tested using unpaired Student's t test. **, p < 0.01; ***, p < 0.001. C, bar diagrams showing a relative reduction in the percentage of pyruvate kinase activity after silencing of PKM1 and PKM2 in H1299 (left panel) and A549 (right panel) cells. D–F, glucose uptake (D), lactate release (E), and intracellular ATP (F) levels in H1299 (left panel) and A549 (right panel) cells stably transduced with vector (pLKO.1), shPKM1, or shPKM2; with statistical analysis (where n ≥ 3; mean ± S.D.) and the level of significance was tested using unpaired Student's t test. *, p < 0.05; **, p < 0.01; ***, p < 0.001.