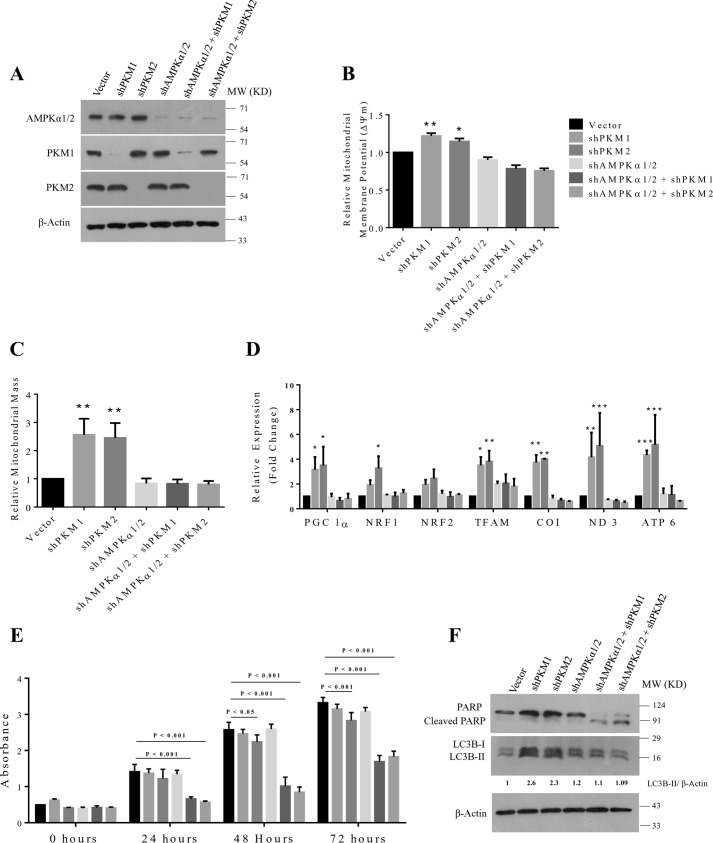
Figure 8.
AMPKα2 and PKM1 or PKM2 dual knockdown induces cell death in H1299 cells by preventing energy metabolism reprogramming. A, immunoblots from the protein lysate of H1299 cells stably transduced with control vector (pLKO. 1), shPKM1, shPKM2, shAMPKα1/2, and shAMPKα1/2 + shPKM1 or + shPKM2 to validate the knockdown of AMPKα1/2, PKM1, and PKM2. B and C, bar diagram depicts the relative mitochondrial membrane potential (B) and mitochondrial mass (C) in H1299 cells stably transduced with control vector (pLKO.1), shPKM1, shPKM2, shAMPKα1/2, and shAMPKα1/2 + shPKM1 or + shPKM2; with statistical analysis (where n ≥ 3; mean ± S.D.), and the level of significance was tested using unpaired Student's t test. *, p < 0.05, **, p < 0.01. D, quantitative RT-PCR analysis to show the relative expression change of genes involved in the mitochondrial biogenesis (PGC 1α, NRF1, NRF2, and TFAM) and mitochondrial-encoded subunits of electron transport chain complexes (COX 1, ND3, and ATP6) from H1299 cells for stable shPKM1, shPKM2, AMPKα1/2, or AMPKα1/2 and PKM1 or PKM2 knockdown. The bars represent the -fold change after normalizing with the control of each group (vector transfected); with statistical analysis (where n ≥3; mean ± S.D.), and the level of significance was tested using two-way analysis of variance with Tukey's multiple comparisons test. *, p < 0.05; **, p < 0.01; ***, p < 0.001. E, CCK8 assay to examine the viability rate of H1299 cells stably transduced with control vector (pLKO.1), shPKM1, shPKM2, shAMPKα1/2, and shAMPKα1/2 and shPKM1 or shPKM2 and cultured for the period of 72 h. Cellular viability rates were assayed for every 24 h; with statistical analysis (where n ≥ 3; mean ± S.D.), and the level of significance was tested using two-way analysis of variance with Tukey's multiple comparisons test. F, immunoblots from the protein lysate of H1299 as mentioned in (A) to measure autophagy and apoptosis using LC3B-II and cleaved PARP as markers.