Figure 4. Cyclopamine treatment reduces frequency and severity of coloboma in zic2 mutants.
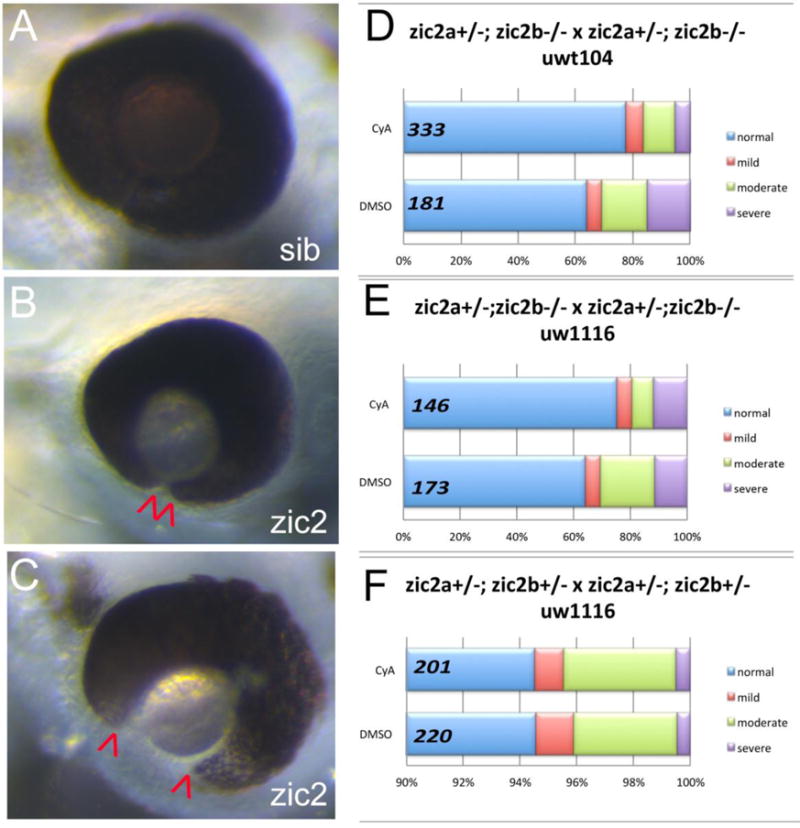
A: normal retinal morphology; B: retina with mild coloboma; C: retina with moderate coloboma. D: Embryos were derived from zic2agbt133/+; zic2b t104 parental crosses and exposed to 3 or 4.5 μM cyclopamine (CyA) from 3–5 hpf until 24–26 hpf. In CyA-treated groups (3 expts; Fig. S3A), the proportion of embryos with coloboma was reduced significantly compared to vehicle-treated control siblings (Fisher’s Exact test, P < 0.001). Proportion of severely affected embryos among all embryos with coloboma was also decreased in CyA-treated siblings (Fisher Exact test, p<0.02). E: Embryos were derived from zic2agbt133/+; zic2b uw1116 parents, and treated starting at 3 hpf with 4.5 uM Cya. CyA-treated groups exhibited reduction in coloboma penetrance (Fisher’s Exact test p<0.04) compared to vehicle-treated control siblings (2 expts; Fig. S3B). F: Embryos were derived from zic2agbt133/+; zic2b uw1116/+ parents, and treated as in D with 4.5 uM CyA or vehicle starting at 3 hpf. Proportion of embryos with coloboma was not affected by exposure to cyclopamine (2 expts). Embryos with unilateral mild coloboma were scored as “mild”; embryos with bilateral mild coloboma were scored as “moderate”, and embryos with bilateral moderate coloboma were scored as “severe”.
