Figure 1.
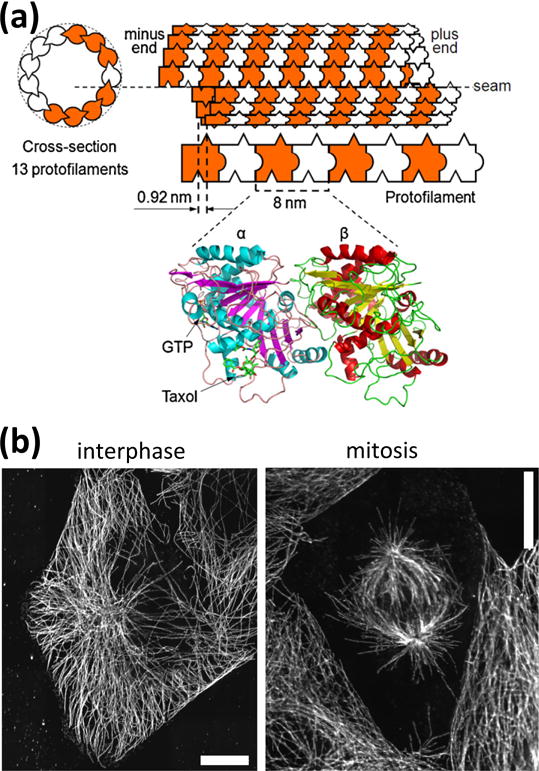
(a) Schematic representation of a microtubule with 13 protofilaments. Protofilaments are made from tubulin dimers which bind to each other in a head-to-tail fashion. Protofilaments bind to each other with an offset which results in a seam in the microtubule structure. The ribbon diagram (bottom) is derived from electron crystallography4 and shows the GTP and taxol binding sites. (b) During interphase, the microtubule cytoskeleton is radially organized, with microtubules emerging from a microtubule-organizing center located in the vicinity of the nucleus (visible as the microtubule free central region). During mitosis, two spindles of oriented microtubules form, then the microtubules attach to the chromosomes initially located along the centerline of the dividing cell and separate them by exerting forces generated from depolymerization. Scale bars: 10 μm.
