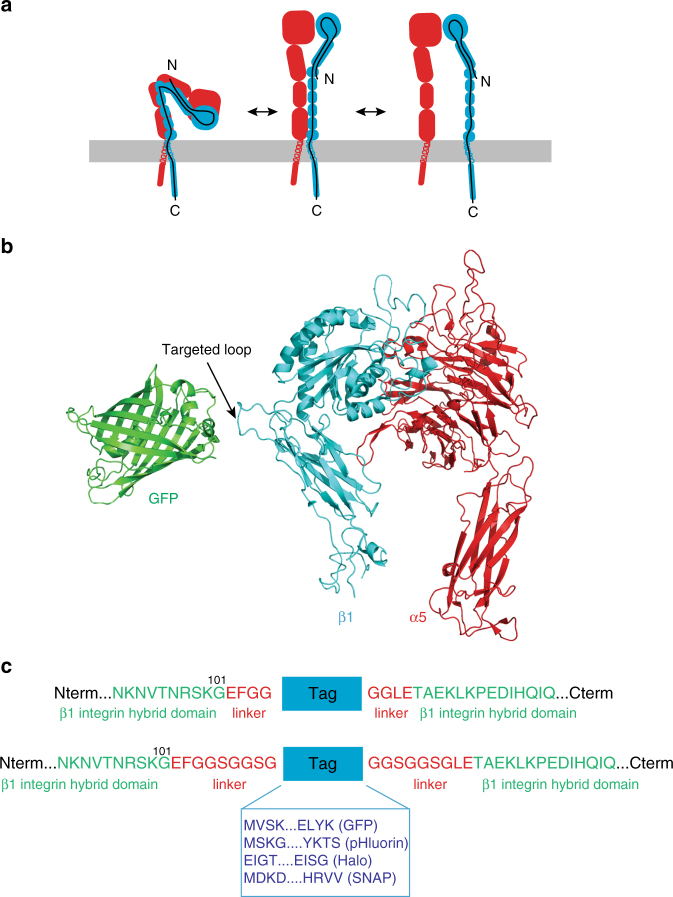
Fig. 1.
Design of an ecto-tagged β1 integrin. a Cartoon of the conformational changes in the integrin heterodimer during integrin activation; α subunit is depicted in red, β subunit in blue, and the black line represents the β subunit polypeptide chain. b Ribbon diagram of the crystal structures of the α5β1 integrin head piece (PDB: 3VI4) and GFP (PDB: 1GFL). The hybrid domain loop into which ecto-tags were inserted is indicated. c Zoom-in on the amino acid sequence of human ecto-tagged β1 integrins at the tag insertion site. Each ecto-tag (GFP, pHluorin, Halo, and SNAP, in blue, N- and C-terminal sequences specified) was inserted into the hybrid domain of human β1 integrin between residues Gly101 and Tyr102 (in green). Linkers of 4 or 9 amino acids (in red) were added on each side of the tag to facilitate cloning and provide flexibility