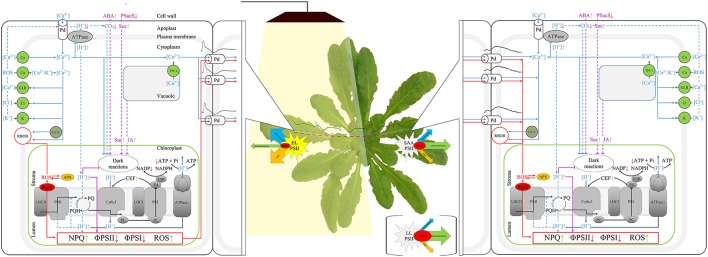
Figure 1.
Scheme of the signaling pathways triggered by electrical signals, that are possibly involved in long-term adjustment of photosynthesis, SAA and SAR. The blue solid lines indicate the induction of the calcium wave; blue dotted lines—fast pathways influencing photosynthesis; purple lines - the pathways for long-term inactivation of photosynthesis; red lines—ROS- and NPQ-dependent pathways, sinus-like wave—the electric signals, black solid lines—electron flow. Abbreviations in the alphabetical order: ABA, abscisic acid; APX, ascorbate peroxidase; arrows, increase (green) and decrease (red) of a process; ATPase, ATP synthase; C/C-C, Ca2+- dependent protein kinases (CPK/CBL-CIPKs); Ca, potential-dependent, mechano-sensitive and (or) ligand-dependent Ca2+ channels; CEF, cyclic electron flow; Cl, Ca2+- dependent Cl− channels; Cyt b6f, cytochrome b6f complex; EL, excess light; FD, ferredoxin; FNR, ferredoxin-NADP+ reductase; GLR, Glue receptor-like channels; JA, jasmonic acid; K, potential-dependent K+ channels; LHCII and LHCI, Light-harvesting complex II and I; LL, low light; NPQ, non-photochemical quenching; Pd, plasmodesma; PQ and PQH2, oxidized and reduced plastoquinone; PsbS, Photosystem II Subunit S; PSII and PSI, photosystems II and I; PSucS, phloem sucrose symporter; RBOH, Respiratory oxidase homolog; SAA, systemic acquired acclimation; Suc, sucrose; TPC1, vacuolar TWO PORE CHANNEL1 calcium channels; ΦPSI and ΦPSII, the photochemical quantum yield of PSI and PSII.