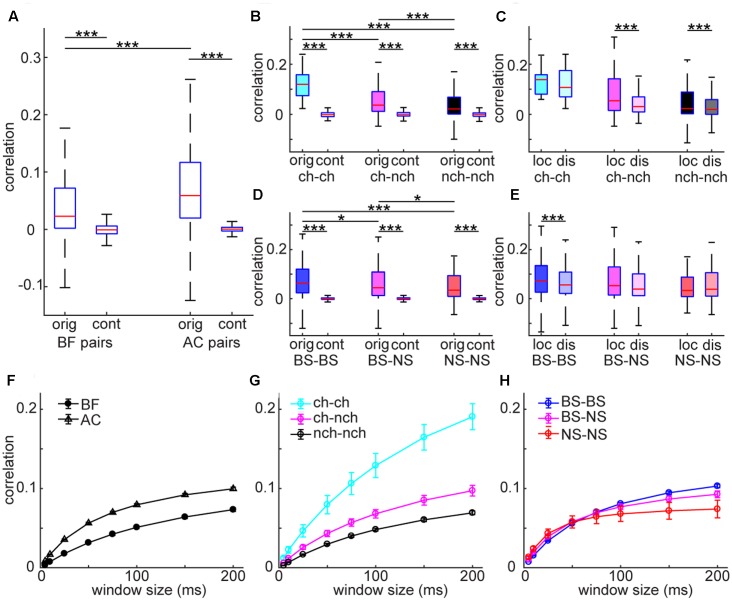
FIGURE 5.
Spike count noise correlations in BF and AC neuron pairs. (A) Comparison of correlations between BF and AC pairs. As a control (cont), surrogate data was generated by using the raster marginals model. The effect of pair was highly significant (F3,74455 = 1148, p < 0.00001, one-way ANOVA). ∗∗∗p < 0.00001 (post hoc HSD test). orig, original correlations; cont, control. (B,D) Comparisons of correlations across different types of cell pairs in the BF (B) and AC (D), with control. The effect of pair type was significant in both the BF (F5,30761 = 1628, p < 0.00001), and AC (F5,43686 = 5323, p < 0.00001). Cholinergic cell pairs showed higher correlations compared to other pairs (p < 0.05). ∗∗∗p < 0.0001 (post hoc HSD test within pair types). ch, cholinergic neurons; nch, non-cholinergic neurons. (C,E) Comparisons of correlation between local (≤150 μm) and distal (>150 μm) pairs across different types of cell pairs in the BF (C) and AC (E). In the BF (C), the effect of pair type was significant (F2,2791 = 16.6, p = 6.56e–08, two-way ANOVA) whereas the effect of distance was not (F1,2791 = 3.68, p = 0.054). A significant interaction of pair type and distance was observed (F2,2791 = 4.52, p = 0.010). In the AC, no effect of pair type (F2,3966 = 1.34, p = 0.25) or distance (F1,3966 = 1.16, p = 0.27) was detected whereas a significant interaction of pair type and distance was observed (F2,3966 = 3.03, p = 0.048). ∗∗∗p < 0.0001 (post hoc HSD test within pair types). (F–H) Dependency of window size on spike count correlations. (F) Spike count correlations of BF and AC cell pairs across window sizes. (G) Spike count correlations of different cell pairs in the BF across window sizes. (H) Spike count correlations of different cell pairs in the AC across window sizes.