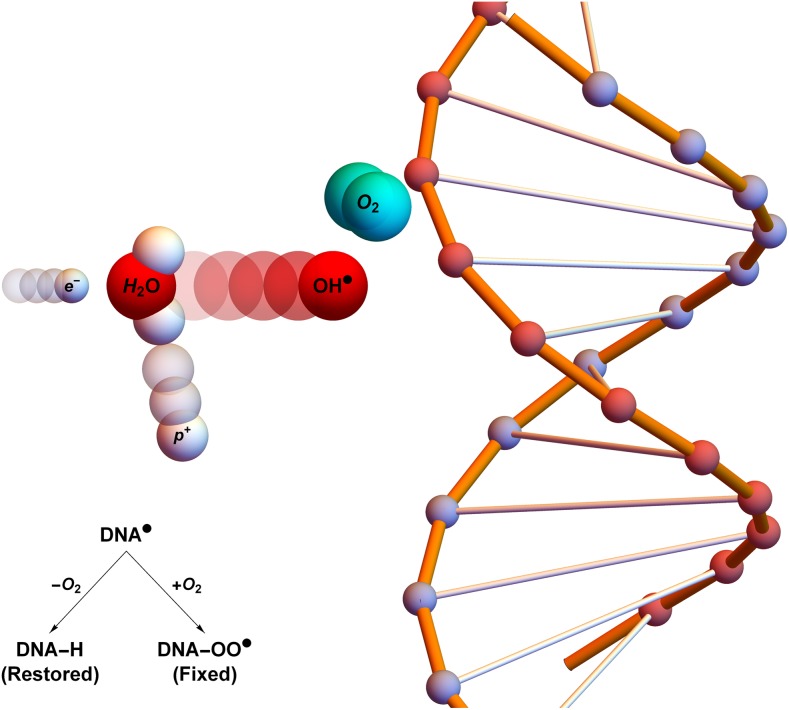
Figure 3.
Oxygen fixation hypothesis: a high-energy electron created by an X-ray photon (e−) impinges on a water molecule, liberating a proton (p+) and creating a hydroxyl radical (OH˙). This reactive molecule then impacts on deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA˙), resulting in ionization damage, DNA. This can be readily repaired to its original state (DNA-H), but in the presence of molecular oxygen, a peroxy radical is formed (DNA-OO˙), fixing damage into a permanent irreparable state. Taken from Grimes and Partridge with permission from Institute of Physics (IOP).16