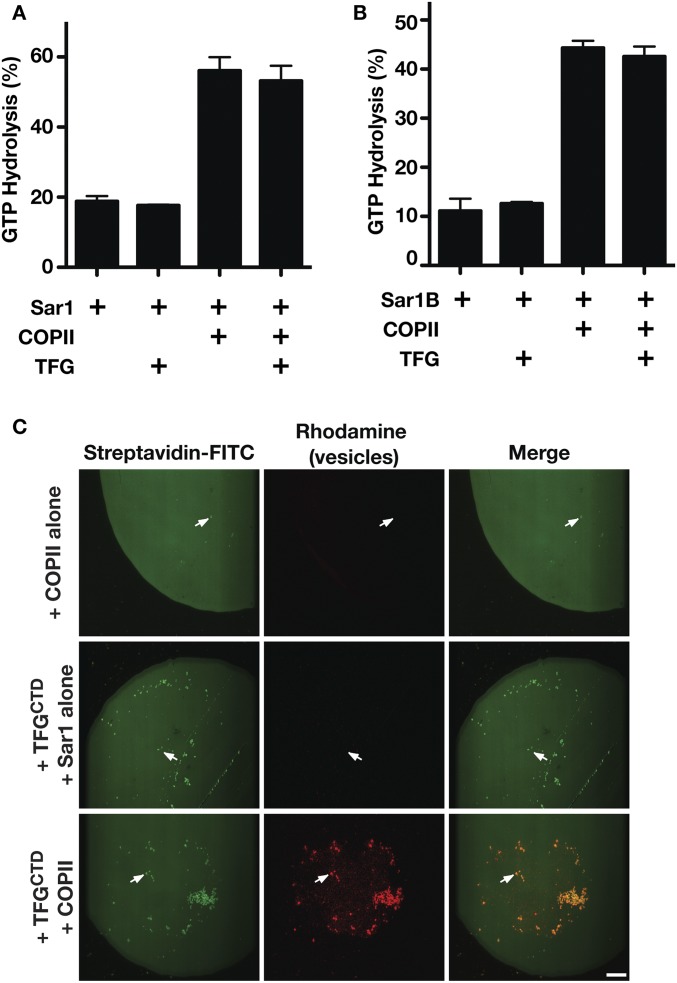
Fig. S7.
The TFG C terminus does not promote Sec23-mediated GAP activity on Sar1 but is capable of tethering COPII-coated liposomes. (A) C. elegans TFG (amino acids 196–486) was incubated with Sar1 loaded with GTP in the presence or absence of Sec23-Sec24, and the extent of GTP hydrolysis was measured (n = 3). (B) Human TFG (amino acids 194–400) was incubated with Sar1B loaded with GTP in the presence or absence of Sec23A-Sec24A, and the extent of GTP hydrolysis was measured (n = 3). (C) Microcontact printing was used to generate biotinylated surfaces to which FITC-streptavidin was bound. Incubations in the presence or absence of the C. elegans TFG C terminus (amino acids 196–486) fused to the streptavidin-binding peptide and liposomes containing rhodamine-PE that were coated either with Sar1GTP and Sec23 (COPII) or with Sar1GTP alone were conducted. Surfaces were inverted onto glass coverslips and imaged using confocal microscopy (n = 3). Arrows highlight streptavidin-labeled structures, which only localize with rhodamine-labeled vesicles in the presence of TFG and COPII. (Scale bar, 25 μm.)