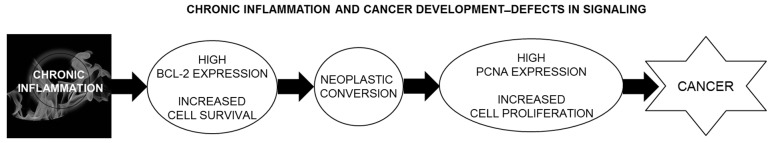
Figure 6.
A hypothetical model showing how chronic inflammation leads to cancer development. Under the influence of chronic inflammation epithelial cells acquire increased survival with an increase in Bcl-2 expression. The survival signal alters the phenotype of these particular epithelial cells, which gain neoplastic characteristics, leading to precursors that may later acquire increased proliferation rate leading to cancer development and subsequent progression.