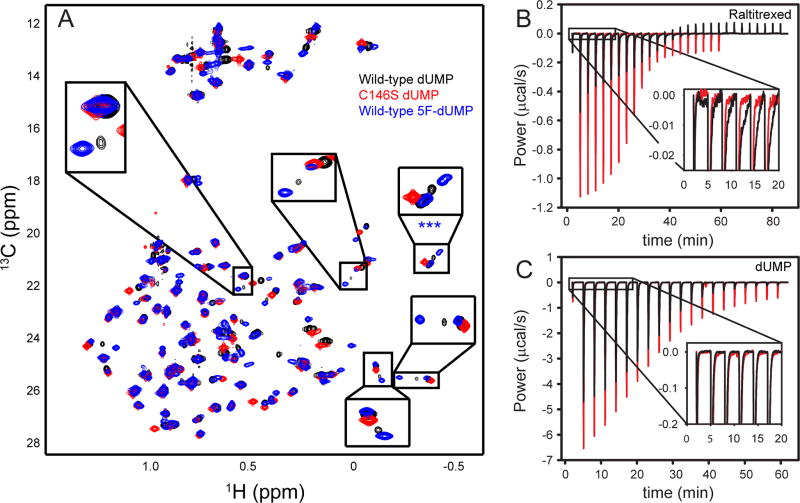
Figure 2.
A fraction of the TSase-dUMP complex contains a covalent bond between C146@Sγ and dUMP@C6. (A) ILV methyl 1H-13C HSQC spectra of the wild-type dUMP complex (black), C146S-dUMP complex (red), and wild-type 5F-dUMP complex (blue). Expanded boxes contain resonances that report on a minor state with a covalent bond between C146 and dUMP (see text). Note the minor state is more highly populated in the 5F-dUMP complex and absent in the C146S complex. Note also that the C146S-dUMP complex resonances overlay with the major state resonances of the wild-type-dUMP complex. (B) ITC thermograms for Raltitrexed binding to the wild-type and C146S-dUMP complexes in black and red respectively. The expanded region shows a slow exothermic component in the wild-type, but not the mutant thermogram, that is therefore likely to report on covalent bond formation. (C) ITC thermograms for wild-type and C146S dUMP binding are colored similarly to panel B. Expanded baseline shows ITC does not detect covalent bond formation in either of these titrations.