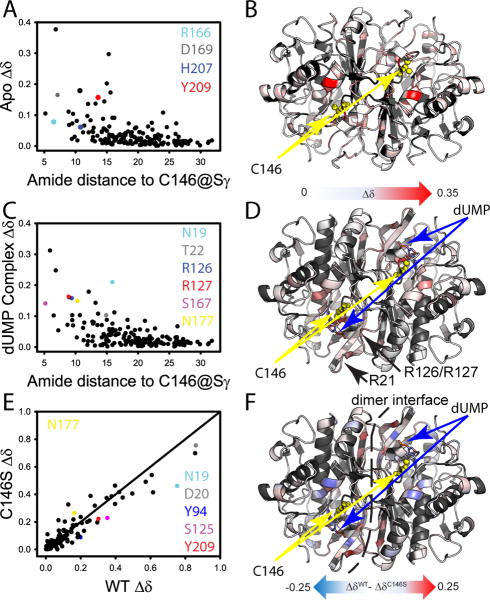
Figure 4.
Effect of C146S mutation on free and dUMP-bound TSase from NMR amide chemical shifts. (A)Mutational CSPs (See Experimental Procedures) in the apo-enzyme are plotted vs the distance to the site of mutation. Residues important to dUMP binding and discussed in the text are highlighted in color. (B)CSPs from panel A are mapped onto the apo-enzyme structure with the site of mutation in yellow. (C) Mutational CSPs in the dUMP complex are plotted vs the distance to the site of mutation. Residues important to dUMP binding and discussed in the text are highlighted in color. (D) CSPs from panel D are mapped onto the dUMP-complex structure with the site of mutation and substrate highlighted. The CSP scales in Panels B&D are the same. The phosphate binding arginine loops are highlighted in this panel. (E) The CSPs for wild-type dUMP binding are plotted against the CSPs for C146S dUMP binding. Important residues having different CSPs associated with complex formation are highlighted in color. (F) The difference in CSP is mapped onto the dUMP complex structure. The model is annotated to show significant differences in the binding site and dimer interface.