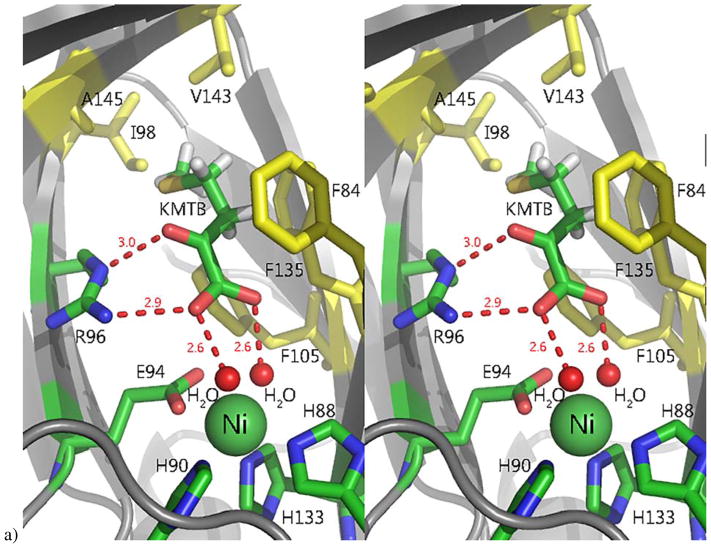
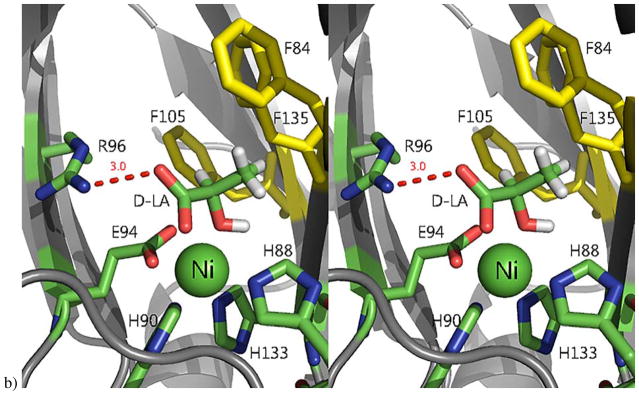
Figure 7. The active site of Ni-MmARD showing substrate-analog and product binding.
The Ni atom is shown as a green sphere, the ligands and active site residues are shown as sticks and waters/hydroxides are shown as small red spheres. Hydrogen bonding distances are shown (in Å) as red dotted lines. Hydrophobic residues in the active site are shown in yellow. a) Stereo view of KMTB bound to Ni-MmARD. KMTB is within hydrogen bonding distance of Arg96 and the two water molecules ligated to Ni. The residues Phe84, Phe105, Phe135, Ala145, Val143 and Ile98 interact with the alkyl group of KMTB. b) Stereo view of D-Lactic acid (D-LA) bound to Ni-MmARD. D-LA replaces both equatorial water ligands, coordinating in a bidentate manner with Ni2+ via the carboxylate and hydroxyl oxygens. D-LA is within hydrogen bonding distance of Arg96. Residues Phe84, Phe105 and Phe135 interact with the alkyl group of D-LA. (Adapted from Ref 3. Copyright 2016 American Chemical Society).