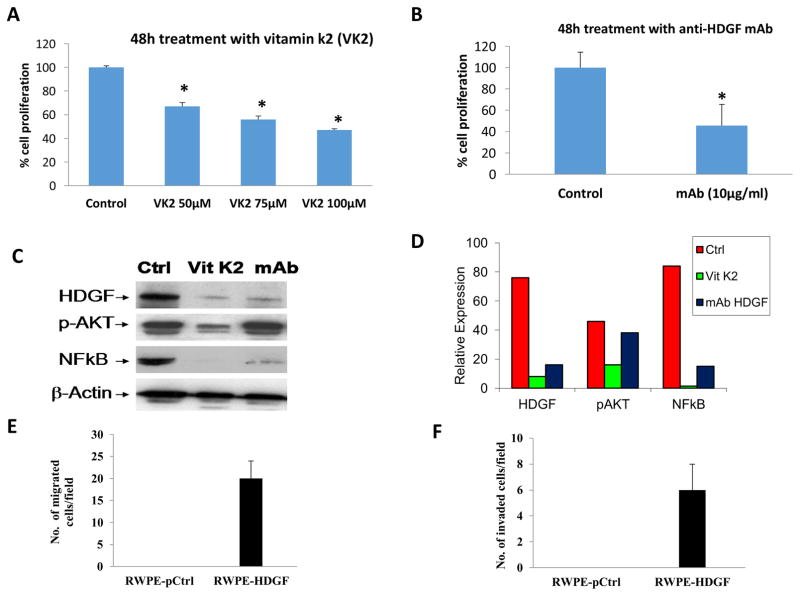
Figure 6.
HDGF inhibitors decrease the proliferation of RWPE-1 cells transformed with HDGF. RWPE-1 cells expressing HDGF (RWPE-HDGF) were seeded in 96 well plates. At 50% confluency, cells were treated with either Vitamin K2 (50–100 μM) or a monoclonal antibody specific to HDGF (10 μg/ml) for 48h. Untreated cells served as a control. At the end of treatment, the viability of the cells was determined by cell viability assay as described in materials and methods. Results show that both Vitamin K2 and the monoclonal antibody to HDGF significantly decreased the proliferation of RWPE-HDGF cells. *p<0.05 compared to control groups. Down regulation of HDGF expression in RWPE-HDGF cells by vitamin k2 and mAb results in the inhibition of NFκB (p65). RWPE-HDGF cells treated with Vitamin K2 or mAb for 48h were subjected to Western blot analysis. Results presented in C and D show that both Vitamin K2 and mAb treatment inhibited the expression of HDGF leading to down regulation of its target molecule NFκB (p65) in the RWPE-HDGF cells. Notably downregulation of pAKT was observed with vitamin k2 treatment but not with mAb treatment. HDGF expression increases migration and invasion of RWPE-1 cells. E) To determine the overexpression effects of HDGF on migration and invasion of RWPE-1, cells were transfected with HDGF plasmid for 48h and subjected to in vitro migration and invasion assays. Briefly, RWPE-1 cells overexpressing HDGF (RWPE-HDGF) were seeded on Transwell chambers for 24h and studied for its ability to migrate. F) RWPE-HDGF cells were also seeded on Transwell chambers coated with matrigel for 24h to monitor their invasion potential. Results show that HDGF expression conferred the migration and invasion properties to normal RWPE-1 cells.