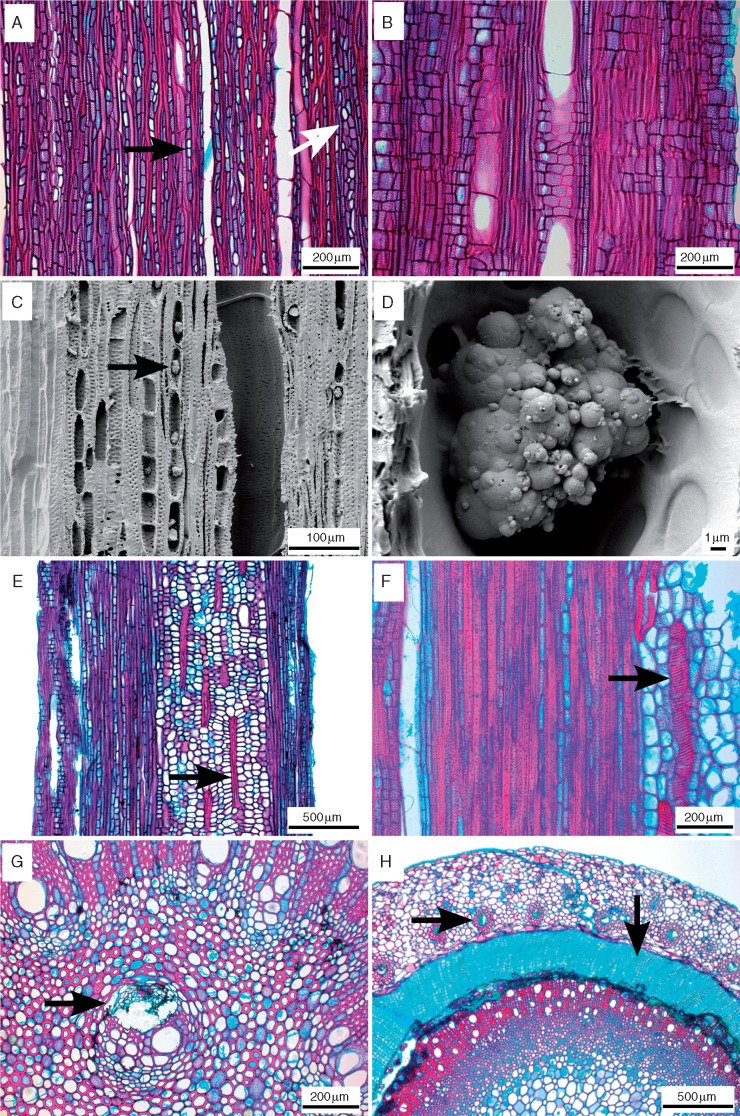
Fig. 2.
Light microscope sections of tangential (A), radial (B, E) and transverse (F, G, H) views, and scanning electron microscope images (C, D) of tangential surfaces of Nepenthes wood. (A) Nepenthes khasiana, overview showing dense uniseriate (black arrow) and narrow multiserate rays (white arrow). (B) Nepenthes gymnamphora, overview of rays with mainly square to upright ray cells. (C, D) Nepenthes ampullaria, abundant silica grains in ray cells (arrow). (E) Nepenthes reinwardtiana, thick-walled, helically banded sclereids within the pith (arrow). (F) Nepenthes burbidgeae, detail of thick-walled, helical idioblast in pith (arrow). (G) Nepenthes tobaica, medullary bundle (arrow). (H) Nepenthes ventricosa, cortical vascular bundles inside cortex (horizontal arrow), deep-seated periderm with cork cylinder (vertical arrow).