Figure 6.
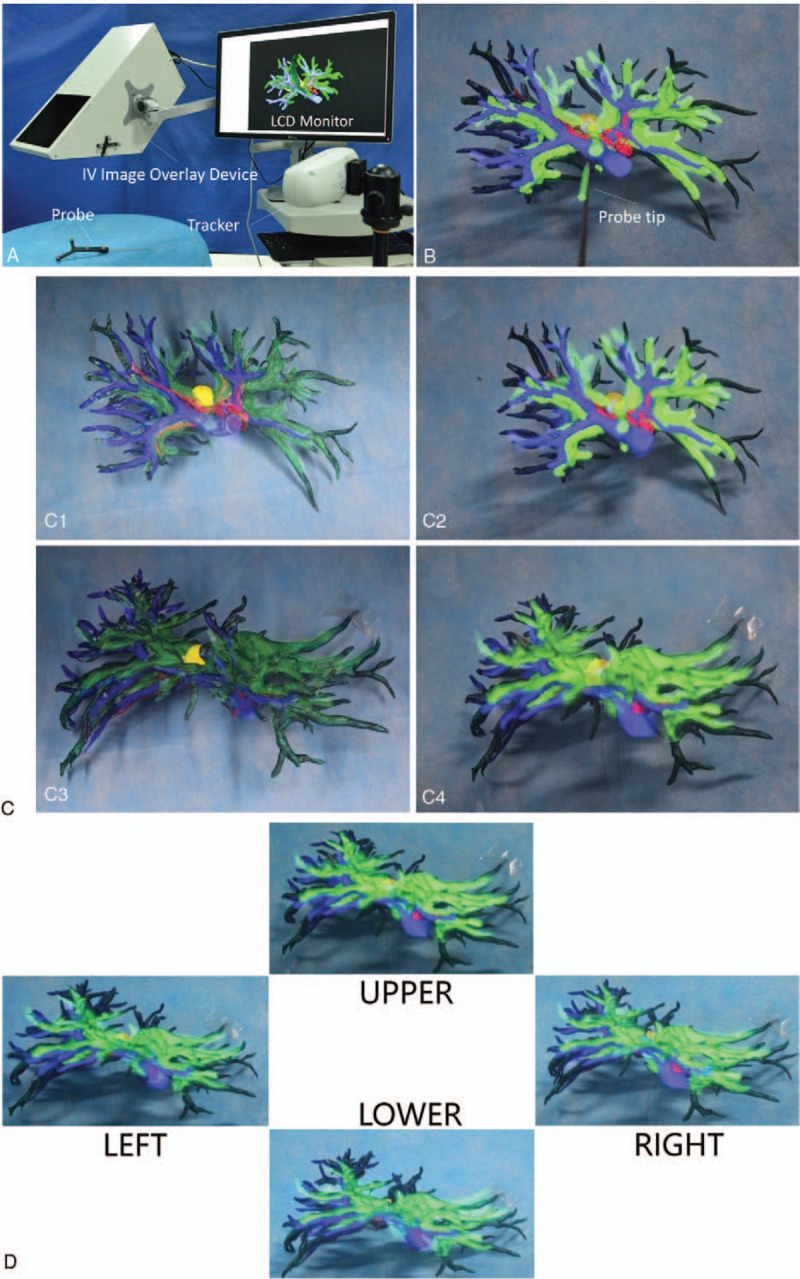
Evaluation of the imaging characteristics of autostereoscopic see-through display using IV. (A) The patient's reconstructed preoperative 3D images were superimposed onto the 3D-printed model using IV overlay device, and LCD monitor. (B) Four vessel bifurcations in the 3D model were designated as anatomical landmarks using an optical tracker and probe. (C1–C4) Rigid registration was performed, aligning these 4 points with the corresponding locations in the reconstructed 3D images. (D) Peering through the viewing window of the IV image overlay device, the surgeons viewed the 3D model and in situ superimposed 3D images from 4 slightly different orientations to estimate whether depth perception and motion parallax were improved, compared with that which they had experience using the video-based display method for intraoperative navigation.
