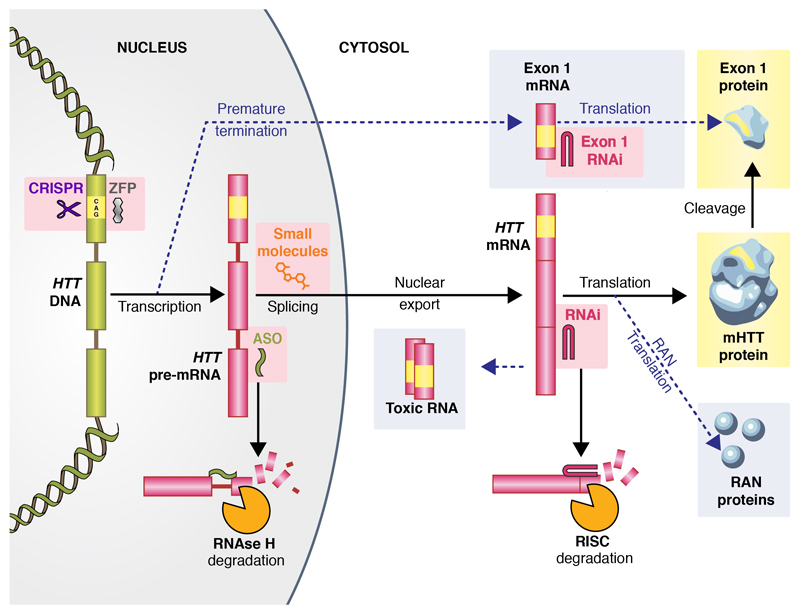
Figure 1.
The production of huntingtin protein, and targeted molecular therapies in development to reduce it. Yellow marks the pathogenic expanded CAG tract and its polyglutamine product. Therapeutic approaches are highlighted with pink boxes. Yellow boxes indicate the most widely accepted toxic species. Dotted arrows and grey boxes indicate proposed non-traditional mechanisms for the production of toxic species. The chief mechanisms of action of ASOs and RNAi compounds are shown at the bottom. The image of huntingtin protein is adapted from reference 24 under a creative commons licence (CC-BY-4.0).