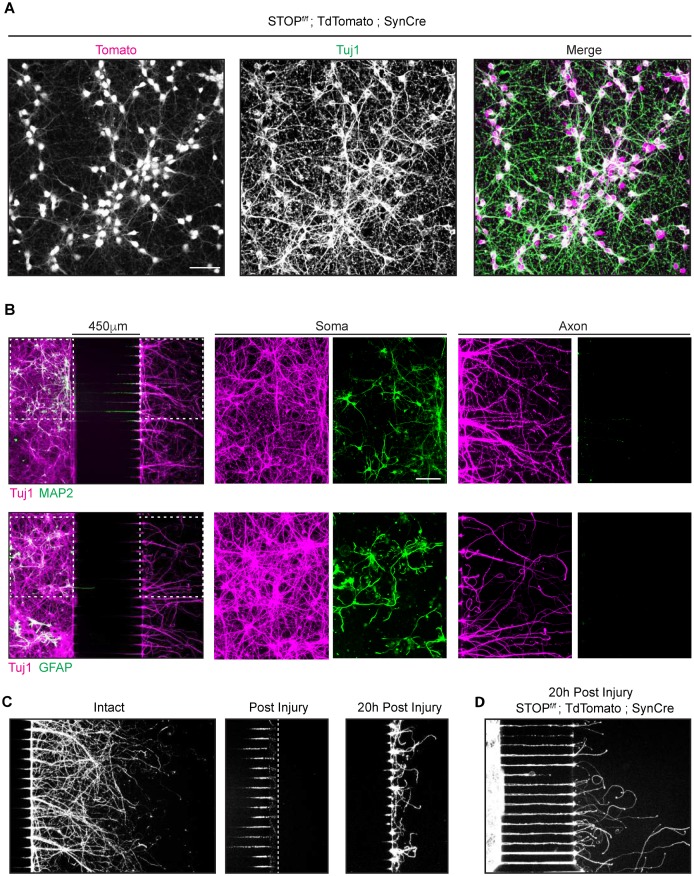
Fig 1. Characterization of Synapsin Cre in neurons cultured in microfluidic chambers.
(A) Immunohistochemistry of cortical neurons (DIV6) isolated from Synapsin Cre; stopf/f TdTomato transgenic mice. Anti Tuj1 antibody was used as a neuronal marker. TdTomato (magenta in the merged image) is present in almost all the neuronal cell bodies. Scale bar = 50μm. (B) Immunohistochemistry using Tuj1 (axonal marker, magenta), MAP2 (dendrite marker, green first row) or GFAP (glial cell marker, green second row) antibodies on E18 mouse cortical neurons culture (DIV7) in microfluidic chambers. Higher magnifications images of somal and axonal compartments are shown in the second and third columns. Neurons were plated in the chamber on the left and their axons grew through the grooves in the center section to emerge in the axonal chamber at the right. 450 μm microgrooves allows a complete isolation of axons from dendrites and glia as indicated by the absence of those markers from the right-hand chamber. Antibodies typically did not reach inside the microgrooves unless explicitly caused to enter (not shown), which is why grooves remain largely dark. Scale bar = 100μm (C) Tuj1 immunohistochemistry of E18 mouse cortical neurons cultures (DIV7) in microfluidic chambers: No Injury (left), immediately after injury (center) and 20 h after injury (right). (D) E18 mouse cortical neurons cultures from Synapsin Cre; stopf/f TdTomato embryo culture fixed 20 h post axonal injury.