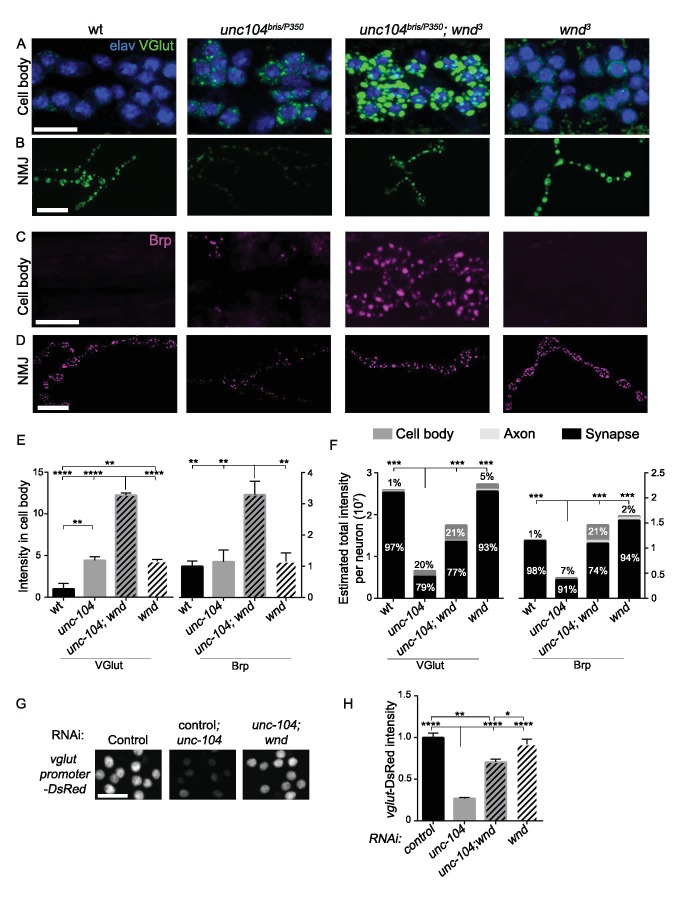
Figure 7. Wnd restricts the expression level of presynaptic components Brp and VGlut in unc-104 mutants.
(A–D) Immunostaining for VGlut (green, (A and B) and Brp (magenta, (C and D) in motoneuron cell bodies (A and C) and NMJ terminals (B and D). In (A) motoneuron nuclei are indicated by Elav staining (blue). Note the increased intensity of VGlut and Brp in unc-104bris/P350; wnd3 double mutants. (E) Quantification of VGlut and Brp intensity in cell bodies of motoneurons, corresponding to images in A and C. Note that total intensity measured at NMJ terminals is shown in Figure 2E–F. (F) Estimates generated for the total levels of VGlut and Brp proteins within motoneurons, accounting for the summed intensities measured in cell body, axonal, and synaptic compartments. Methods and assumptions used to calculate these estimates are described in Experimental Procedures. These proteins predominantly localize to the NMJ synaptic terminals (the proportion of the total protein localized to synapses is indicated with black shading). In unc-104-hypomorph mutants, a larger percentage is detected in cell bodies (medium gray shading), and the total summed intensity is reduced. In unc-104; wnd double mutants, the intensity increases in all of the compartments, cell body, axon (light gray shading) and synapse, compared to unc-104 mutants alone. Wt animals are Canton S. (G) Images of motoneuron nuclei, immunostained for DsRed in vglut promoter-DsRed reporter lines. (H) Quantification of vglut-DsRed intensity in (G), normalized to controlRNAi (moody RNAi). UAS-RNAi lines were driven by OK6-Gal4. For cell body analysis, at least 2 dorsal abdominal clusters of motoneurons per animal from at least 6 animals per genotype were examined. All data are represented as mean ±SEM; ****p<0.0001, ***p<0.001, **p<0.01, *p<0.05, Tukey test for multiple comparison; Scale bar, 20 μm. For additional data, see Figure 7—figure supplements 1–3.
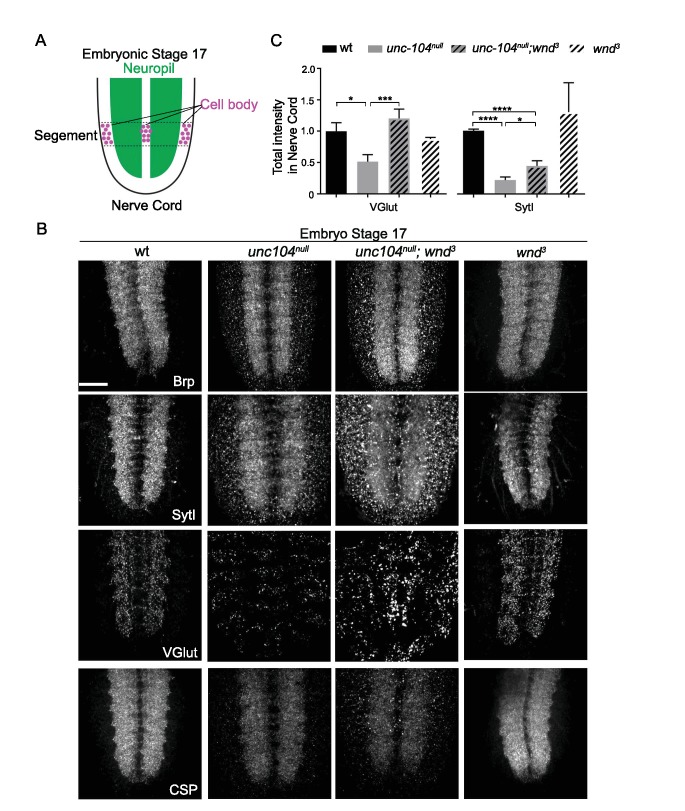
Figure 7—figure supplement 1. In unc-104-null mutants, multiple synaptic proteins were down-regulated by Wnd, (related to Figure 7).
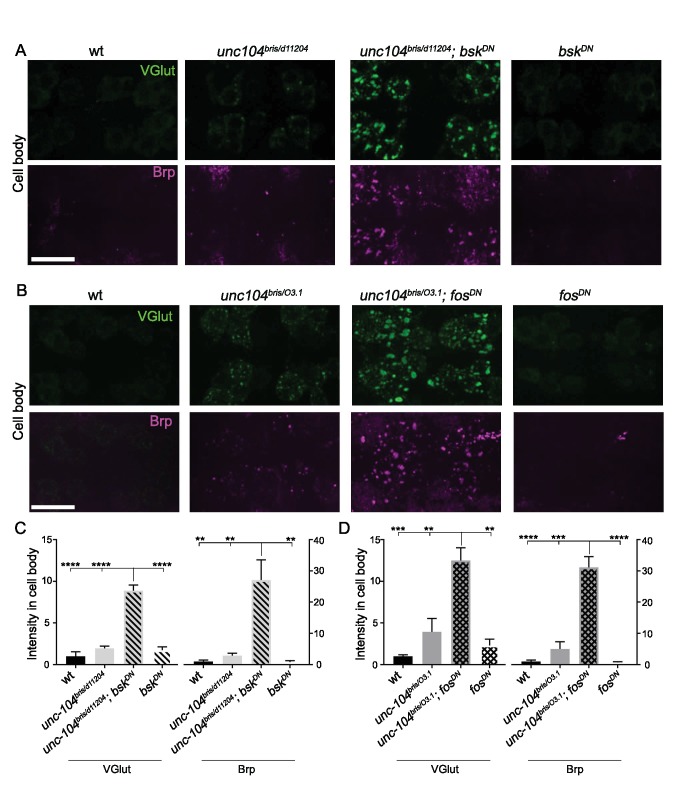
Figure 7—figure supplement 2. Wnd signaling components JNK/Bsk and Fos restrict the expression level of presynaptic components Brp and VGlut in cell bodies of unc-104 mutants, (related to Figure 7).
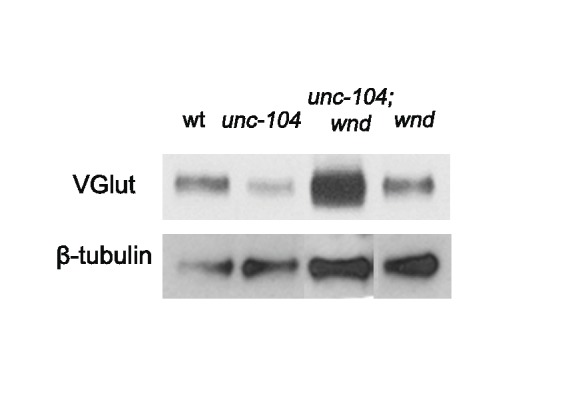
Figure 7—figure supplement 3. Total VGlut protein levels are reduced in unc-104-hypomorph mutants, in a Wnd-dependent manner (related to Figure 7).