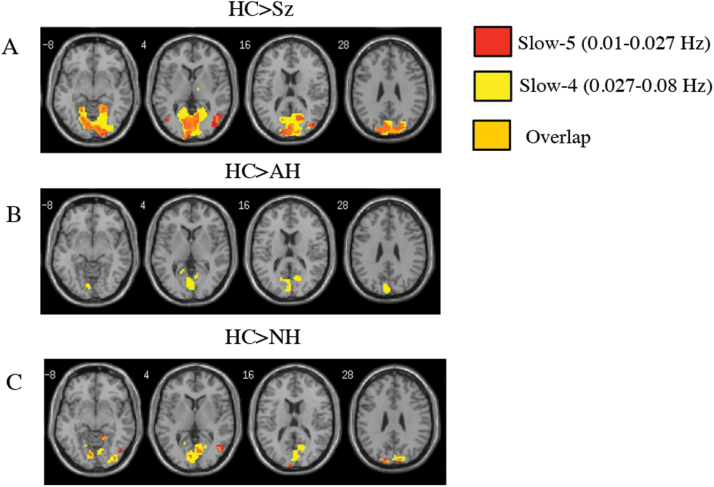
Fig. 1.
Patients with auditory hallucinations and non-hallucinators show similar decreases in ALFF in the back of the brain in comparison to healthy subjects. (A) t-contrast (HC>Sz), (B) t-contrast (HC>AH), and (C) t-contrast (HC>NH). This same pattern of reduced ALFF in the posterior brain was not seen in the HC>VH+AH contrasts. All contrasts are thresholded at P < .05, FWE-corrected, masked with the main effect of group (P = .001 uncorrected) with an extent threshold of k = 10 voxels. HC, healthy control; Sz, schizophrenia; AH, auditory hallucinations; NH, non-hallucinator; VH, visual hallucinations; ALFF, amplitude of low-frequency fluctuations.