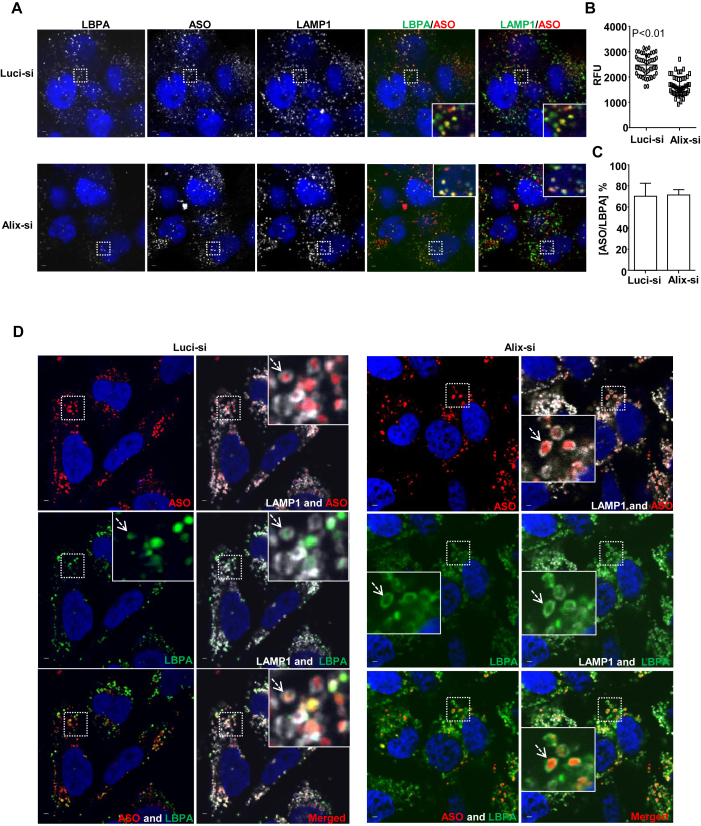
Figure 7.
Alix reduction decreases LBPA levels and diminishes co-localization of LBPA with PS-ASOs at ILVs. (A) Representative images of immunofluorescent staining for LBPA (green) and LAMP1 (green) in control- or Alix-siRNA treated A431 cells, which were further incubated with Cy3-labeled PS-ASOs (red) for 2 h. The nuclei were stained with DAPI (blue). Scale bar, 5 μm. (B) Intensities of LBPA in 20 LEs from each of 15 cells were quantified and normalized to intensities of LAMP1 using FV10-ASW 3.0 viewer. P < 0.01, Alix-si versus Luci-si. (C)The PS-ASO-positive organelles co-stained with LBPA were also counted in 20 Luci- or Alix-siRNA treated A431 cells. The percentage of the organelles positive for both PS-ASOs and LBPA was calculated relative to the total numbers of the PS-ASO-positive organelles. (D) Representative images of immunofluorescent staining for LBPA (green) and LAMP1 (gray) in Luci- or Alix-siRNA treated HeLa cells, which were further treated with YM201636 after the incubation with Cy3-labeled PS-ASOs (red) for 4 h. The nuclei were stained with DAPI (blue). Scale bar, 5 μm.