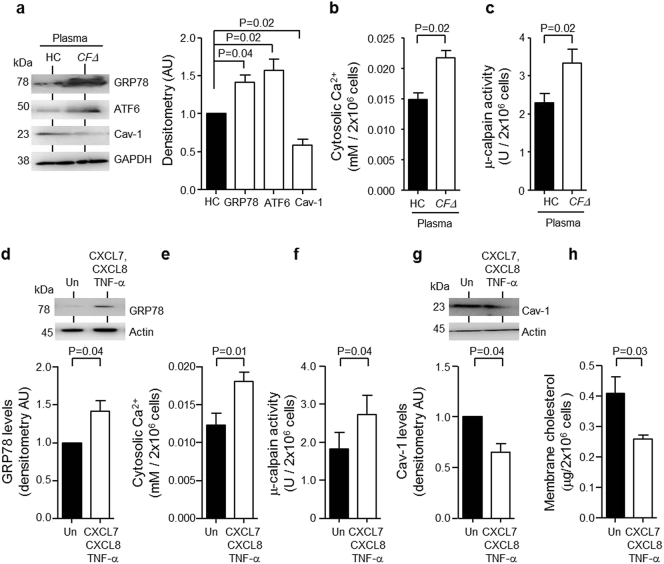
Fig. 4.
Inflammatory induced ER stress results in degradation of Cav-1.
HL-60 cells (2 × 106) were cultured for 24 h in 20% (v/v) pooled plasma from HC (plasma pool of n = 3 individuals) or patients with CF homozygous for the ΔF508 mutation (CFΔ, plasma pool of n = 3 patients). (a) Treated HL-60 cells were lysed and purified cytosols subjected to Western blot analysis for GRP78, ATF6 or Cav-1. Significantly increased GRP78 and ATF6, yet significantly decreased Cav-1 protein levels were detected (P = 0.04, P = 0.02 and P = 0.02 respectively, n = 3 independent experiments, Student's t-test). (b and c) Significantly increased cytosolic Ca2 + and μ-calpain activity were detected in cytosols of HL-60 cells exposed to CFΔ plasma compared to HC plasma (P = 0.02, n = 3 independent experiments, Student's t-test). (d-h) HL-60 cells (2 × 106) were exposed to a combination of CXCL7 (10 μg/ml), CXCL8 (200 pg/ml) and TNF-α (400 pg/ml) for 24 or 72 h and cytosols and membranes were purified. (d) Western blot and densitometry analysis revealed significantly increased cytosolic GRP78 (P = 0.04, n = 3 independent experiments, Student's t-test) in cells exposed to CXCL7, CXCL8 and TNFα for 24 h. (e and f) HL-60 cells exposed to pro-inflammatory mediators had significantly elevated cytosolic Ca2 + and μ-calpain activity (P = 0.01 and P = 0.04 respectively, n = 3 independent experiments, Student's t-test) at 24 h. (g) Cytosolic Cav-1 (P = 0.04, n = 3 independent experiments, Student's t-test) and (h) membrane cholesterol content (P = 0.03, n = 3 independent experiments, Student's t-test) were significantly reduced in HL-60 cells treated with CXCL7, CXCL8 and TNFα for 24 and 72 h, respectively. Each measurement in the mean ± SEM.