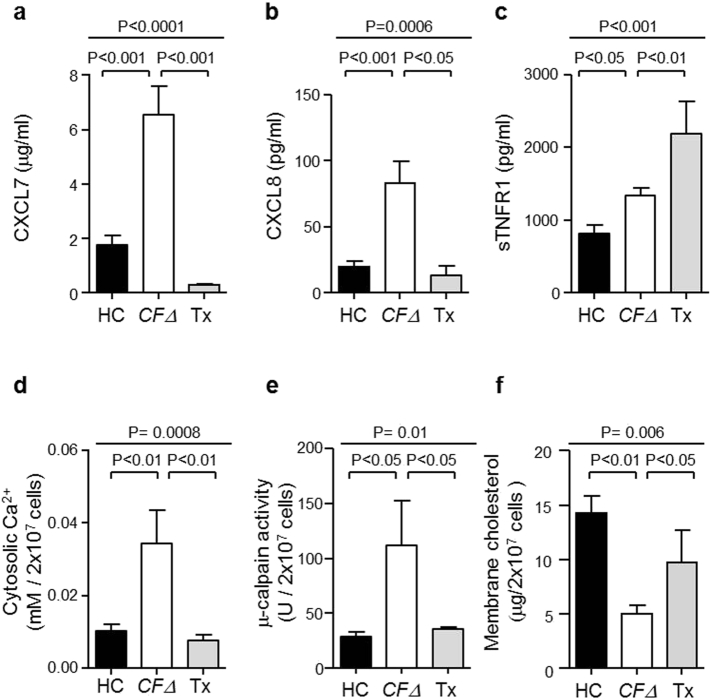
Fig. 5.
Lung transplant treatment reduced levels of circulating inflammatory mediators.
(a–c) ELISA analysis for CXCL7, CXCL8 and sTNFR1 demonstrated significantly increased plasma levels in CFΔ compared to HC (P < 0.001 and P < 0.05, respectively, n = 6 subjects per group, Student's t-test). Significantly decreased plasma CXCL7 and CXCL8 levels, yet increased levels of sTNFR1 detected post-transplant (Tx) when compared to CFΔ (P < 0.001, P < 0.05 and P < 0.01, respectively, n = 6 subjects per group, Student's t-test). (d) Analyses of neutrophil cytosols for Ca2 + revealed significantly increased levels in CFΔ compared to HC cells (P < 0.01, n = 6 subjects per group, Student's t-test), and significantly decreased levels in Tx (P < 0.01, n = 6 subjects per group, Student's t-test). (e) μ-calpain activity was significantly elevated in CFΔ cytosols compared to HC samples (P < 0.05, n = 6 subjects per group, Student's t-test) and significantly decreased in TX (P < 0.05, n = 6). (f) Plasma membrane cholesterol content was significantly reduced in CFΔ compared to HC samples (P < 0.01, n = 9 subjects per group, Student's t-test) and significantly increased in Tx (P < 0.05, n = 4 subjects per group, Student's t-test). Each measurement is the mean ± SEM.