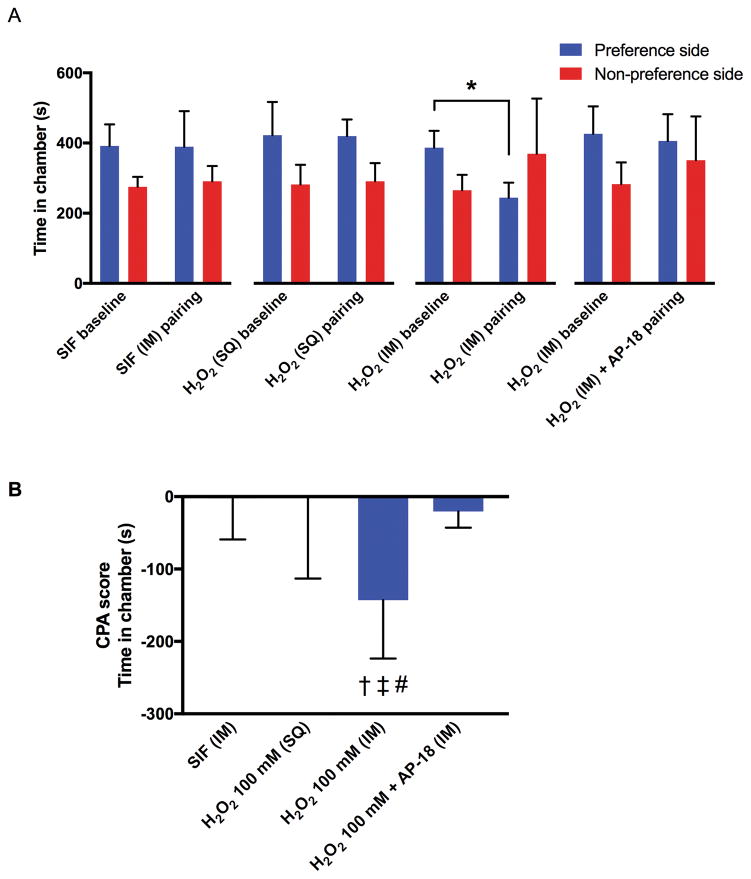
Fig. 2. The effects of intramuscular (IM) or subcutaneous (SQ) injection of H2O2 (100 mM, 0.6 ml) on conditioned place aversion (CPA) in rats.
Each column represents the time spent in the preferred and non-preferred chambers during the pre- and post-conditioning sessions (A), and the CPA scores (B). For the intramuscular co-injection of H2O2 and AP-18, sequential injections of AP-18 (50 mM, 0.3 ml) followed by H2O2 (200 mM, 0.3 ml), were made into the gastrocnemius muscle. Therefore, the total injection volume was 0.6 ml, and the final concentration of H2O2 was 100 mM. Each group contained six rats. All data are expressed as means ± SD. * P = 0.0075 by paired t-test. † = 0.0199 compared with the SIF group, ‡ P = 0.0194 compared with the subcutaneous injection of H2O2 group, # P = 0.0479 compared with the intramuscular co-injection of H2O2 and AP-18 group by one-way ANOVA (F3, 20 = 4.884, P = 0.0104) followed by post-hoc Tukey’s test.